Add By Counting On - Sums Up To 20
Subject: Math
Grade: First grade
Topic: Addition Strategies Up To 20
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
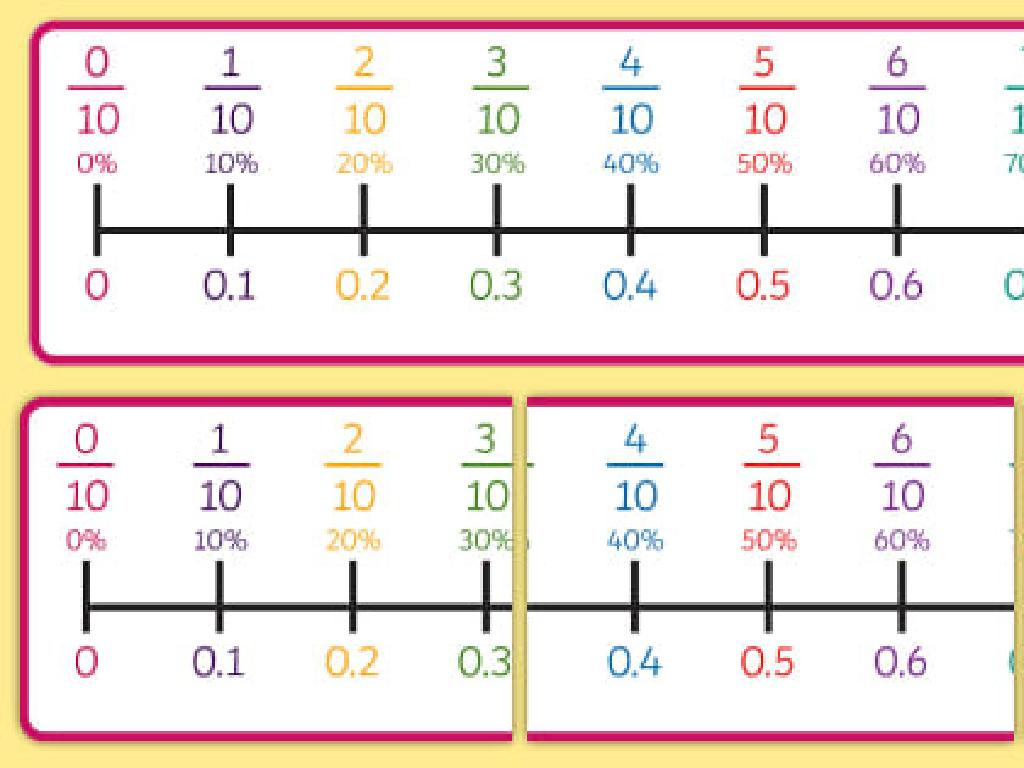
Welcome to Addition: Counting On!
– Learning addition is fun!
– Addition finds the total number
– If you have 3 apples and get 2 more, addition tells you have 5 apples in total.
– Counting on to add numbers
– Start with the bigger number and count up. For 5 + 3, say ‘five’ and count ‘six, seven, eight’.
– Practice sums up to 20
– We’ll do examples together like 7 + 5 and 6 + 4.
|
This slide introduces first graders to the concept of addition as a fun and practical skill. Emphasize that addition is a way to find out the total amount of something. Demonstrate ‘counting on’ as a strategy where they start with the larger number and count up to add the second number. Use hands-on activities with physical objects like blocks or counters to practice this skill. Encourage students to use their fingers to count on when adding numbers together. Prepare several examples that sum up to 20 or less to practice as a class, ensuring that students understand the concept before moving on to independent work.
Learning to Add by Counting On
– Understanding Counting On
– Counting on means adding small numbers to a bigger one.
– Start with the biggest number
– If we have 5 and add 3, start counting from 5… 6, 7, 8!
– Imagine hopping on a number line
– Visualize jumping ahead on the number line for each count.
– Let’s practice with an example
– Example: 7 + 2. Start at 7… then 8, 9. So, 7 + 2 = 9!
|
This slide introduces the concept of ‘Counting On’ as an addition strategy for sums up to 20. It’s important to emphasize starting with the larger number and ‘counting on’ the smaller number. Use a number line graphic to illustrate the ‘hopping’ or ‘jumping’ forward method. Engage the students with a simple example, such as adding 2 to 7, and encourage them to count aloud together. This visual and interactive approach helps solidify the concept and prepares them for practicing more examples in class.
Adding by Counting On: Sums Up to 20
– Start with the biggest number
– Count on to add the smaller number
– Example: Adding 5 and 3
– Begin with 5, then count on 6, 7, 8
– Practice makes perfect!
– Try with different numbers for mastery
|
This slide introduces the concept of ‘counting on,’ a fundamental addition strategy for first graders. Begin by identifying the larger number in the equation, which is more efficient for counting on. Then, demonstrate how to count up from the larger number by the amount of the smaller number. Use the example provided (5 + 3) to illustrate the process, starting from 5 and counting on three more numbers to reach 8. Encourage students to practice this technique with various number combinations to develop fluency in addition up to 20. The goal is for students to become comfortable with this strategy and to use it as a stepping stone to more complex arithmetic.
Your Turn to Count On!
– Start with the number 6
– Add 2 to the number 6
– Count on: 7, 8
– After 6, say 7 then 8
– Discover 6 plus 2 equals 8
– 6 + 2 is the same as counting 7, 8
|
This slide is designed to engage first-grade students in a counting on activity to practice addition up to 20. Begin by presenting the number 6 and then instruct the students to add 2 to it. Guide them through the process of counting on from 6 to reach the sum of 8. Emphasize that adding 2 means counting two numbers forward from 6. Encourage the students to use their fingers or manipulatives to count on. This activity helps to reinforce the concept of addition as a form of counting on. For the class activity, have students practice with different starting numbers and addends, ensuring they understand the concept of counting on to add.
Adding Bigger Numbers by Counting On
– Start with a bigger number, like 10
– Count on 5 more steps from 10
– After 10, say 11, 12, 13, 14, 15
– Each step is one number higher
– 10 plus 5 ends up at 15
– So, when we add 5 to 10, we reach 15
|
This slide is aimed at teaching first graders how to add larger numbers using the counting on strategy. Begin by explaining that starting with a larger number, like 10, they can ‘count on’ to add another number. Demonstrate counting on by physically moving or pointing to numbers on a number line or with objects. Emphasize that each step is one number higher than the last. Use examples like 10 plus 5 to show that when they count on five steps from 10, they will end up at 15. Encourage students to use their fingers or objects to count on from larger numbers and to practice with different combinations that add up to 20 or less.
Let’s Practice Together: Counting On!
– I’ll show you addition problems
– Use fingers or a number line to add
– Start from the first number, then count up
– We’ll solve problems together
– As a team, we’ll find the right answers
– Practice makes perfect
|
This slide is designed to engage students in a collaborative class activity to practice the ‘counting on’ addition strategy. Begin by presenting a few simple addition problems that sum up to 20 or less. Encourage students to use their fingers or a number line, which are tangible tools that help them visualize the counting process. Work through each problem as a class, allowing students to contribute and count on from the larger number. This interactive approach reinforces their understanding of addition and builds confidence. As an extension, consider pairing students up to solve additional problems or using manipulatives like counters or blocks for a hands-on experience.
Counting On Game: Race to 20!
– Pair up for a counting game
– Roll the dice, start from 10
– Add dice number to your total
– If you roll a 4, what’s 10 + 4?
– First to reach 20 wins!
|
This interactive game is designed to help students practice the ‘counting on’ strategy in a fun and engaging way. Each pair of students will need a dice and a way to keep track of their total. Students start at 10, roll the dice, and add the number they roll to their total. They take turns with their partner. The first student to reach or exceed 20 is the winner. For the teacher: Prepare dice for each pair, demonstrate the game with a student, and encourage students to verbalize their counting as they play. Possible variations include using different starting numbers or playing until a different total to differentiate for various skill levels.
Review: Adding by Counting On
– Counting on is fun and easy!
– Start with the biggest number
– If we add 4 + 3, start from 4… then 5, 6, 7!
– Practice to improve skills
– The more we practice, the faster we get
– Let’s count on together!
– We’ll do a class activity to practice counting on
|
This slide is a review of the counting on strategy for addition, which is a fundamental skill for first graders learning to add numbers up to 20. Emphasize the ease and fun of this method to keep students engaged. Remind them that starting with the biggest number makes counting on simpler and more efficient. Encourage regular practice to help them become quicker and more confident in their ability to add. Conclude with a class activity where students can apply this strategy together, reinforcing their learning through collaboration and repetition.
Homework: Practice Counting On!
– Take home your addition worksheet
– Solve problems by counting on
– Start from the larger number and count up
– Complete all the sums up to 20
– Bring it back for review
– We’ll check the answers as a class
|
This homework assignment is designed to reinforce the ‘counting on’ addition strategy learned in class. The worksheet will contain a variety of addition problems that do not exceed the sum of 20. Encourage students to start with the larger number in the problem and ‘count on’ from there. This method helps build mental math skills and number sense. Remind students to complete all the problems and to bring their worksheets back to the next class for a collaborative review session. This will allow you to assess their understanding and provide additional support where needed. Prepare to praise efforts and offer guidance on any mistakes to ensure students feel confident in their ability to use the ‘counting on’ strategy.