Name Countries Of Asia: Review
Subject: Social studies
Grade: Sixth grade
Topic: Asia: Geography
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Exploring Asia: The Largest Continent
– Asia: Earth’s largest continent
– Celebrating Asia’s diversity
– Home to various cultures, languages, and climates
– Countries of Asia: A closer look
– Learn about the 49 countries and their unique features
– Importance of Asian geography
– Understanding Asia’s role in global economy, politics, and culture
|
This slide introduces students to Asia, the largest continent on Earth, both in size and population. Emphasize the vast diversity found within Asia, including a multitude of cultures, languages, and climates. Highlight the significance of learning about the 49 countries that make up Asia, focusing on their distinct characteristics, such as national borders, capital cities, and geographical landmarks. Discuss why it’s important for students to be familiar with different countries in Asia, considering the continent’s growing influence on the world’s economy, political affairs, and cultural exchanges. Encourage students to think about how Asia’s diversity might impact global relationships and their own lives.
Exploring the Countries of Asia
– Total number of countries
– Asia has 49 distinct countries.
– Asia’s regional divisions
– Asia is split into five main regions.
– Countries from each region
– For example, China in East Asia, India in South Asia.
– Review and discussion
– We’ll recap and talk about what we’ve learned.
|
This slide aims to provide a broad overview of the countries in Asia, their count, and regional divisions. It’s important to highlight that Asia, being the largest continent, has a diverse range of cultures, languages, and governments. The five regions are Central Asia, East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Western Asia. Provide examples like China, India, Kazakhstan, Thailand, and Saudi Arabia to represent each region respectively. Encourage students to think about the diversity within these regions and to be ready to discuss the countries they know or have learned about in this review session.
Exploring East Asia
– Countries of East Asia
– China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, Taiwan
– China: The Great Wall
– The Great Wall of China can be seen from space!
– Japan: Land of the Rising Sun
– Japan is known for its advanced technology and cherry blossoms.
– Mongolia: The Nomadic Culture
– Mongolia is famous for its vast steppes and nomadic traditions.
|
This slide aims to review the countries in East Asia and share interesting facts to spark students’ curiosity. Start by identifying each country on a map. For China, discuss the significance of the Great Wall and its historical importance. When talking about Japan, mention its unique blend of ancient traditions and modern technology. Highlight Mongolia’s nomadic culture and how it has shaped their society. Encourage students to think of other fun facts they may know about these countries or to research more about them. This activity will help students remember the countries and associate them with memorable cultural aspects.
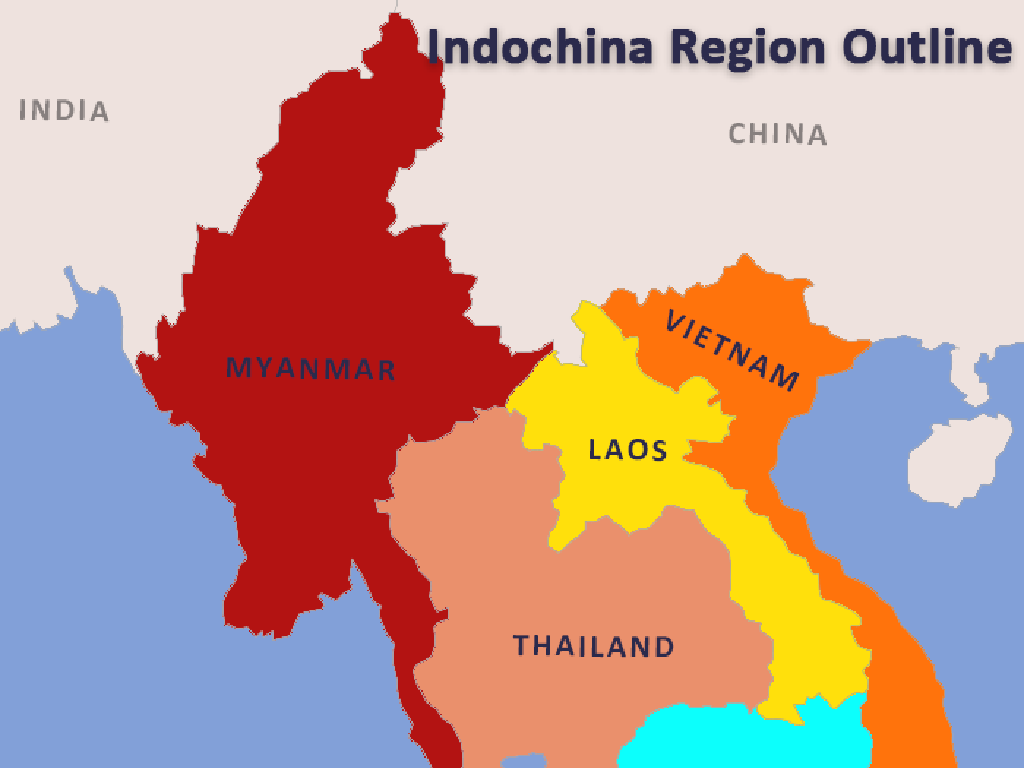
Exploring Southeast Asia
– Countries of Southeast Asia
– Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Vietnam
– Unique geography of the region
– It’s a region of peninsulas and islands, featuring diverse landscapes from rainforests to mountains.
– Cultural diversity
– Economic significance
|
This slide aims to introduce students to the countries of Southeast Asia and highlight the region’s unique geographical features. Emphasize the diversity of landscapes, which includes both mainland and island nations, and the importance of the region’s strategic location for global trade. Encourage students to explore the cultural and economic aspects of Southeast Asia, which are deeply influenced by its geography. Provide a map to help students visualize the location of each country and discuss how the geography has shaped the history and development of the region.
Exploring South Asia
– Identify South Asian countries
– Afghanistan to Sri Lanka
– Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka
– Cultural significance
– Rich traditions, diverse languages, and religions
– Historical importance
– Home to ancient civilizations, historical landmarks
|
This slide aims to review the countries of South Asia and their importance. Students should be able to identify the eight countries that make up South Asia. Emphasize the rich cultural diversity found in this region, including a variety of languages, religions, and traditions. Discuss the historical significance of South Asia as the birthplace of several ancient civilizations and the location of many historical landmarks. Encourage students to think about how geography can influence culture and history. Provide examples such as the Indus Valley Civilization in Pakistan and the cultural heritage of India’s Taj Mahal.
Exploring Central Asia
– Countries of Central Asia
– Five nations: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan
– Kazakhstan to Uzbekistan
– Largest to smallest: Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan
– Historical Silk Road
– Ancient trade route connecting Asia with Europe
– Impact on the region
– Silk Road facilitated cultural and commercial exchanges
|
This slide aims to review the countries of Central Asia and their significance in history, particularly through the Silk Road. Start by identifying the five countries in Central Asia, emphasizing their location and any unique geographical features. Discuss the historical importance of the Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes that connected the East and West, and its impact on the development of the countries it passed through. Highlight how the Silk Road was not only a means for trading goods like silk and spices but also ideas, technology, and culture. Encourage students to think about how such historical trade routes have shaped the modern world and the connections between different regions.
Exploring Western Asia
– Countries in Western Asia
– Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cyprus, Georgia, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, UAE, Yemen
– Key economic roles of the region
– Connects major economies, influences oil prices
– Major exports: oil and technology
– Oil-rich countries like Saudi Arabia, technology in Israel and UAE
– Strategic location for trade
– Crossroads of Europe, Africa & Asia, vital for shipping routes
|
This slide aims to review the countries in Western Asia and discuss the region’s significant impact on global economics. Students should be able to identify the countries listed and understand the region’s contribution to the world through its natural resources, technological advancements, and strategic geographic position. Emphasize the importance of oil exports from countries like Saudi Arabia and the growing tech industries in Israel and the UAE. Highlight Western Asia’s role as a trade hub due to its location at the intersection of three continents. Encourage students to think about how this region connects to global markets and the implications for international relations and economics.
Exploring Asia: Countries, Culture, and Economy
– Recap of Asian countries
– Fun facts about each region
– For example, Japan’s cherry blossoms, China’s Great Wall
– Geography’s impact on culture
– Traditions, food, and lifestyles vary with landscapes
– Geography influencing economy
– Resources and trade routes shape economic growth
|
Begin with a quick review of the countries in Asia, ensuring students can identify them on a map. Share intriguing facts about different regions, such as unique landmarks, traditional festivals, or natural wonders, to pique students’ interest. Discuss how the diverse geography of Asia, from the Himalayas to the islands of Indonesia, influences the cultural practices and daily lives of its people. Highlight how geographic features like rivers, mountains, and proximity to oceans have historically affected where people settle, what they eat, and how they earn a living, thus shaping the economies of Asian countries. Encourage students to think about how their own environment influences their daily life to draw parallels.
Class Activity: Mapping Asia
– Label a blank map with Asian countries
– Use maps and flags for identification
– Work in pairs to complete the map
– Discuss your findings with the class
|
This interactive class activity is designed to help students familiarize themselves with the geography of Asia by labeling a blank map with the names of the countries. Provide students with blank maps and sets of flags to assist them in identifying each country. Encourage them to work in pairs to foster collaboration and discussion. As they work, they should use the resources to match flags to countries and correctly label them on the map. After completing the map, each pair will discuss what they’ve learned about the countries of Asia, including any interesting facts or observations. This activity will help reinforce their knowledge of Asian geography and enhance their ability to recognize countries by shape and flag. Possible variations of the activity could include focusing on capitals, major cities, or landmarks to provide additional layers of learning.