Which Sentence Is More Formal?
Subject: Language arts
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: Author'S Purpose And Tone
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Understanding Author’s Purpose and Tone
– Define author’s purpose and tone
– Author’s purpose is the reason for writing; tone is the attitude conveyed.
– Importance of formality in writing
– Recognizing formality helps understand the context and intended audience.
– Formal vs. informal tone examples
– ‘I regret to inform you’ (formal) vs. ‘Sorry, but’ (informal).
– Analyzing tone in literature
– How does tone influence the meaning behind the text?
|
This slide introduces the concepts of author’s purpose and tone, emphasizing the importance of formality in writing. Understanding why an author writes a piece (to inform, persuade, entertain, or explain) and the tone they use (the attitude towards the subject or audience) is crucial for proper interpretation. Students should learn to distinguish between formal and informal tones, as this can affect the message’s reception. Provide examples to illustrate the difference and encourage students to analyze the tone in various texts to better grasp the author’s intent and the nuances of language.
Formal vs. Informal Tone in Writing
– Define Formal Tone
– Formal tone is polite, professional, and serious.
– Define Informal Tone
– Informal tone is conversational and casual.
– Characteristics of formal writing
– Formal writing uses complex sentences, advanced vocabulary, and avoids contractions.
– Characteristics of informal writing
– Informal writing is more personal, uses simple expressions, contractions, and can include slang.
|
This slide aims to help students distinguish between formal and informal tones in writing. A formal tone is typically used in professional or academic settings and is characterized by a more serious and respectful language, while an informal tone is more casual and used among friends or in relaxed environments. When comparing the two, focus on sentence structure, word choice, and the use of contractions or slang. Provide examples of both tones and encourage students to identify the tone in various texts. This understanding will aid them in choosing the appropriate tone for their own writing, depending on the context and audience.
Identifying Formal Tone in Sentences
– Characteristics of formal language
– Formal language uses complex sentences and advanced vocabulary.
– Examples of formal vs. informal
– ‘I am delighted to accept your invitation.’ vs. ‘Cool, I’ll come over!’
– Practice identifying tone
– Analyze sentences to determine the level of formality.
– Discuss importance of tone
– Tone affects how the message is perceived by the reader.
|
This slide aims to help students recognize the formal tone in writing, which is often used in academic and professional settings. Key characteristics include the use of complete sentences, a more sophisticated vocabulary, and the avoidance of contractions and slang. Provide clear examples contrasting formal and informal sentences to illustrate these points. During the practice activity, students should analyze given sentences to identify formal tones, discussing why certain choices in language contribute to a formal or informal tone. Emphasize that understanding the author’s purpose and the intended audience is crucial in determining the appropriate level of formality in writing.
Identifying Informal Tone in Sentences
– Characteristics of informal language
– Use of slang, contractions, and colloquialisms
– Examples of informal tone
– ‘Hey, what s up?’ vs. ‘Good morning, how are you?’
– Practice identifying informal tone
– Analyze sentences to distinguish the informal tone
|
This slide aims to help students recognize the informal tone in writing, which is often characterized by a casual or conversational style. Key features include the use of slang, contractions, and colloquial expressions. Provide clear examples of informal sentences and contrast them with their formal counterparts. During the practice activity, students will analyze given sentences to identify informal elements. Encourage them to explain why a sentence is informal and how it could be rewritten in a formal style. This exercise will enhance their understanding of the author’s purpose and tone, crucial for effective communication.
Formal vs. Informal Sentences
– Compare formal and informal tones
– ‘I need this done ASAP’ vs. ‘Please complete this task promptly.’
– Context determines tone choice
– Formal for work emails, informal for texts to friends.
– Activity: Refine informal to formal
– Take an informal sentence and rewrite it formally.
– Recognize tone in writing
|
This slide aims to help students distinguish between formal and informal sentences, understanding that the context dictates the appropriate tone. Start by showing examples of sentences with both tones side by side. Discuss scenarios where a formal tone is required, such as in academic writing or professional communication, versus an informal tone, which might be used in personal messages or social media. The class activity involves students taking informal sentences and converting them into a formal tone, enhancing their grasp of the nuances in language. Encourage students to consider word choice, sentence structure, and the level of politeness required by the context. This exercise will improve their ability to recognize and use the appropriate tone in their writing.
Understanding Author’s Purpose and Tone
– Relationship between tone and purpose
– Tone reflects the author’s attitude and purpose in writing.
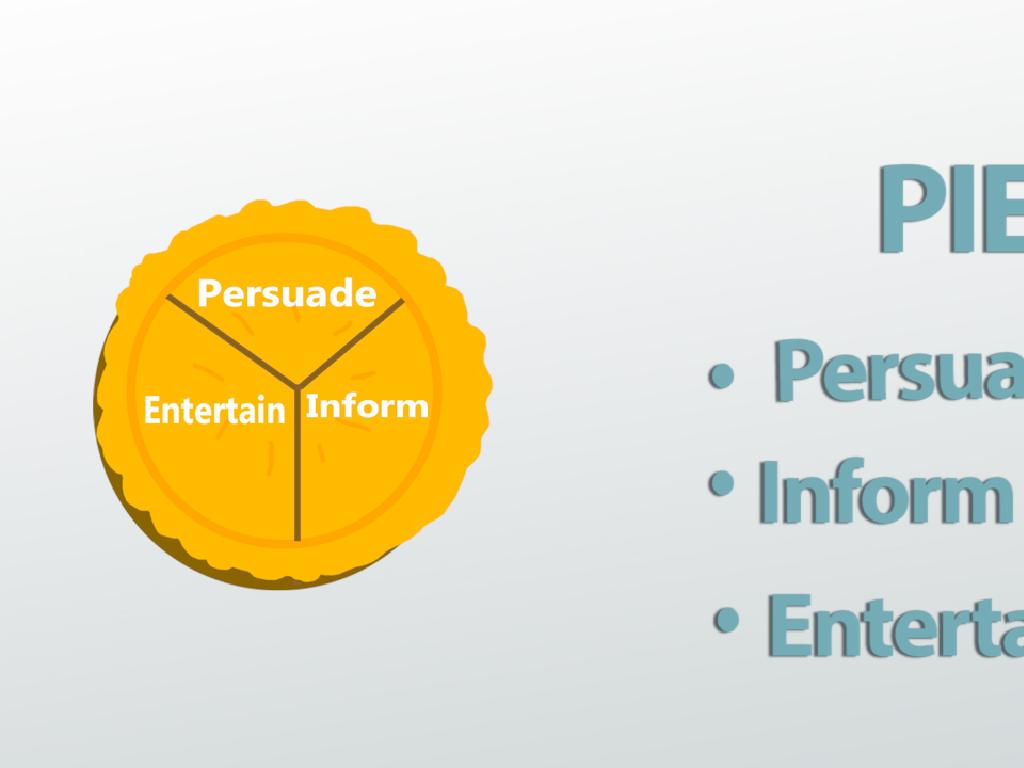
– Exploring reasons for writing
– Authors write to inform, entertain, persuade, or explain.
– Tone’s impact on perception
– The tone can alter how the reader feels about the text.
– Formal vs. Informal tone
– Compare ‘Can you please pass the salt?’ with ‘Pass the salt.’
|
This slide aims to help students understand how an author’s purpose is closely linked to the tone they use in their writing. Tone, the attitude or emotional approach the author takes towards the topic, can greatly affect how the reader interprets the message. Different purposes for writing include informing, entertaining, persuading, and explaining, each of which may require a different tone. For example, a persuasive text may have a passionate tone, while an informative text may be more neutral. Students should learn to analyze the tone to better understand the author’s intent and how it shapes the reader’s perception. The comparison of sentences with different levels of formality illustrates how tone can change the message conveyed. Encourage students to find examples of formal and informal tones in their reading and consider the author’s purpose for choosing each.
Class Activity: Formal or Informal?
– Group activity: Tone identification
– Read texts and determine if the tone is formal or informal
– Each group presents findings
– Share your group’s examples with the class
– Discuss tone’s impact
– How does the tone change the message?
– Reflect on communication
|
This activity is designed to engage students in understanding the concept of tone and its formality in written communication. Divide the class into small groups and provide them with various text excerpts. Their task is to read and decide whether the tone of each excerpt is formal or informal. After the group work, each group will present their findings to the class, explaining their reasoning. This will be followed by a class discussion on how tone affects the way a message is perceived and the importance of choosing the appropriate tone for different contexts. Encourage students to consider how tone can influence the reader’s understanding and the effectiveness of communication. Provide examples of formal and informal tones for the students to use as a reference during their activity.
Wrapping Up: Formal vs. Informal Tone
– Review of formality in writing
– Tone’s role in author’s purpose
– Homework: Craft dual-tone paragraphs
– Write two paragraphs on a chosen topic, one with a formal tone and the other informal.
– Reflect on tone differences
– Consider how word choice and sentence structure affect the formality of your writing.
|
As we conclude today’s lesson, remind students of the key differences between formal and informal writing. Emphasize that the tone of writing is crucial in effectively conveying the author’s purpose, whether it’s to persuade, inform, or entertain. For homework, students should select a topic and write two paragraphs, one formal and one informal, to practice distinguishing between tones. Encourage them to pay close attention to their choice of vocabulary, sentence complexity, and overall structure. In the next class, we’ll discuss how these elements contribute to the formality of their writing and share examples to enhance understanding.