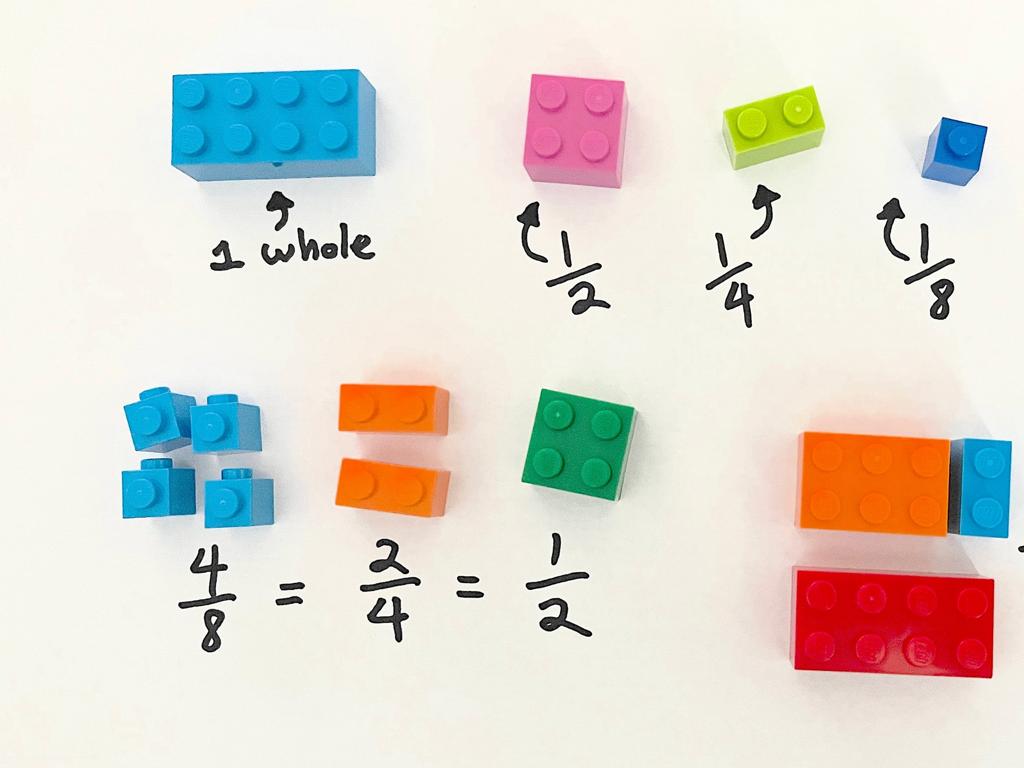Put Decimal Numbers In Order I
Subject: Math
Grade: Fourth grade
Topic: Decimals
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Today’s Adventure: Putting Decimal Numbers in Order!
– Decimals and the ‘dot’ explained
– A decimal has a whole number part, a dot (.), and a fractional part.
– Comparing decimals
– Just like whole numbers, smaller to larger: 0.3 is less than 0.4.
– Practice ordering decimals
– Let’s line up numbers like 0.5, 0.56, and 0.6 in order.
– Real-world use of decimals
– Use decimals when dealing with money, like $0.75 is less than $0.80.
|
This slide introduces the concept of decimals and their importance in everyday life. Start by explaining the components of a decimal number, emphasizing the role of the decimal point. Then, discuss how to compare two decimal numbers by looking at the digits to the right of the decimal point. Engage the students with hands-on practice by having them order sets of decimal numbers. Highlight the practicality of decimals by relating them to money, which is a familiar concept at this age. Encourage students to think of other examples where decimals are used, such as measurements in cooking or science.
Understanding Decimals
– What is a decimal?
– Decimals represent fractions
– A decimal is another way to show parts of a whole, like 0.5 is half
– Splitting a whole into parts
– Imagine cutting a pizza into 10 slices. Each slice is a part of the pizza
– The role of the decimal point
– The dot in numbers like 0.75 is the decimal point, separating whole numbers from the fractional part
|
This slide introduces the concept of decimals to fourth-grade students. Begin by explaining that a decimal is a way to write fractions and parts of a whole number using a decimal point. Use relatable examples, such as dividing a dollar into cents or a pizza into slices, to illustrate how decimals represent parts of a whole. Emphasize the importance of the decimal point, which separates the whole number part from the fractional part. Encourage students to think of decimals as another way to show fractions, making it easier to work with numbers less than one in various mathematical operations.
Ordering Decimal Numbers
– Understand decimal places
– Right of the decimal: tenths, hundredths, etc.
– Places decrease by ten times
– Each place is 10x smaller than the one before it
– Compare decimals to order
– Use place value to determine which is larger
– Practice with examples
– 0.8 vs 0.80, 0.9 vs 0.89
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of decimal places and how to order decimal numbers. Begin by explaining the names of the places to the right of the decimal point and how each subsequent place value is ten times smaller than the one before it. Emphasize the importance of comparing decimals by looking at the highest place value first. Provide examples to illustrate how to compare and order decimals, such as lining up the decimal points and adding zeros to make the numbers easier to compare. Encourage students to practice with additional examples and to explain their reasoning when determining the order of decimal numbers.
Comparing Decimal Numbers
– Decimals can be compared
– Start from the leftmost digit
– Look at the digits in the same place and compare
– Use place value for comparison
– If digits are the same, move one place to the right
– Determine the larger decimal
|
When teaching students to compare decimal numbers, emphasize that the process is similar to comparing whole numbers. Begin by looking at the leftmost digit, which is the highest place value. If those digits are the same, move to the next digit to the right until you find a difference. Use examples like 0.65 and 0.625, comparing digit by digit to see which is larger. Reinforce the concept of place value, as it’s crucial for understanding how to compare decimals. Practice with the class by providing pairs of decimals and working through them together, ensuring students grasp the concept of moving rightward along the number as they compare each place value.
Putting Decimals in Order
– Line up decimals by the point
– Compare digits left to right
– Practice ordering decimals
– Let’s arrange some decimals together!
– 0.3, 0.25, 0.305 example
– Which is smallest? 0.25, 0.3, or 0.305?
|
This slide introduces the concept of ordering decimal numbers. Start by explaining the importance of aligning decimal points vertically before comparing. Emphasize that comparison begins from the leftmost digit and proceeds to the right, just like reading. For the practice example, guide students to see that 0.25 has the smallest value, followed by 0.3, and then 0.305. Encourage students to explain their reasoning for the order they choose. This exercise will help solidify their understanding of decimal place values and comparison. Provide additional examples if time allows and ensure that students are comfortable with the concept before moving on.
Let’s Practice Ordering Decimals!
– Comparing two decimal numbers
– Which is larger: 0.7 or 0.68?
– Is 0.7 bigger than 0.68? Let’s find out!
– Look at the highest place value
– Check the tenths place before the hundredths
– Practice with more examples
– Try ordering 0.52, 0.5, 0.425
|
This slide is an interactive class activity to help students understand how to order decimal numbers. Start by comparing two decimals, 0.7 and 0.68, and guide students to look at the highest place value, which is the tenths place in this case. Explain that since 7 tenths is more than 6 tenths, 0.7 is larger than 0.68 even though 0.68 has more digits. Encourage students to practice with additional examples and to share their reasoning. Provide immediate feedback and support as needed. Possible activities include ordering sets of decimal numbers, using number lines, and peer teaching.
Understanding Tricky Decimals
– Comparing 0.400 and 0.4
– Both numbers have the same value, even though they look different.
– Adding zeros doesn’t change value
– 0.400 is equal to 0.4
– Practice with different decimals
– Try comparing 0.500 with 0.5, or 0.600 with 0.6 to see they are the same.
|
This slide aims to clarify a common confusion among students learning about decimals. Emphasize that adding zeros after the decimal point does not increase the value of the number; it’s simply a placeholder. Use examples on the board to demonstrate this concept, such as lining up the numbers vertically and comparing each decimal place. Encourage students to think of the decimal point as a ‘dot on the spot’ where the spot doesn’t move or change in value with more zeros added to the right. Provide practice examples for students to work on, such as 0.700 vs. 0.7, and ask them to explain why the values are the same. This will help solidify their understanding of decimal place value.
Class Activity: Decimal Ordering Race
– Pair up for a decimal challenge
– Order your set of decimal cards
– Arrange cards from smallest to largest
– First to finish correctly earns a point
– Aim to be the Decimal Champion!
|
This activity is designed to be a fun and interactive way for students to practice ordering decimal numbers. Each pair of students will receive a set of cards with decimal numbers on them. Their task is to work together to arrange these cards in order from the smallest to the largest number. The first pair to correctly complete the task will earn a point for their team. This competitive element will engage students and encourage them to think quickly and accurately. As a teacher, prepare sets of decimal cards in advance, ensure that each set has a mix of numbers with different decimal places, and provide clear instructions. During the activity, circulate to check for understanding and accuracy. After the race, review the correct order of decimals as a class and discuss any common mistakes to reinforce learning.
Ordering Decimals: Conclusion
– Congratulations on learning decimal order!
– Practice is key to mastering decimals
– Continue practicing with home examples
– Try ordering 0.3, 0.56, and 0.6
– Keep up the great work!
|
This slide wraps up the lesson on ordering decimal numbers. Reinforce the concept that understanding how to order decimals is a skill that improves with practice. Encourage students to continue practicing at home with additional examples. Provide them with a few numbers to start with and remind them to look at the place value of each digit when comparing decimals. Celebrate their effort and progress in today’s class and motivate them to keep practicing to become even more confident in their abilities.