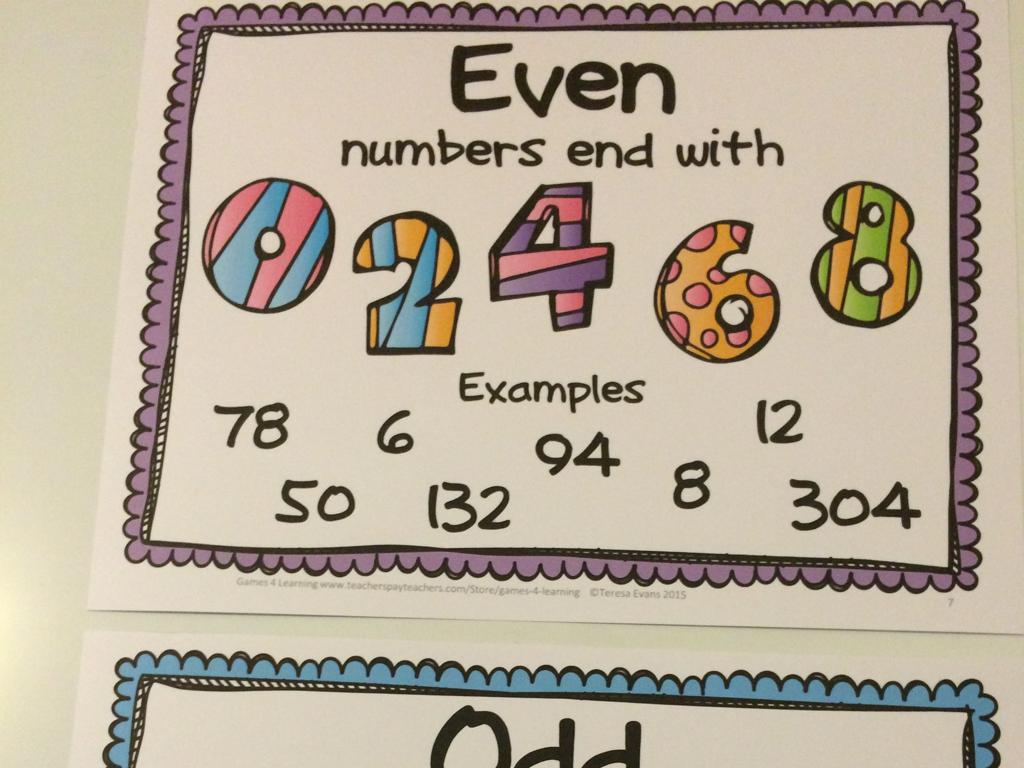Estimate Decimal Quotients
Subject: Math
Grade: Fifth grade
Topic: Divide Decimals
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Estimating Decimal Quotients
– Understand decimals and division
– Decimals represent parts of a whole; division is sharing equally.
– Learn why estimation is useful
– Estimation helps quickly approximate without exact calculations.
– Explore real-life decimal division
– Use in budgeting, measurements, and more.
– Practice with examples
|
This slide introduces the concept of dividing decimals and the importance of estimating decimal quotients. Begin by explaining what decimals are and how division works. Emphasize that estimation is a valuable skill for making quick, reasonable guesses about the result of a division problem without needing a precise answer. Discuss how decimal division is used in everyday life, such as in financial planning or cooking. Provide examples where students can apply estimation, such as determining how much pizza each person gets or splitting a bill. Encourage students to think of other scenarios where they might use decimal division. The goal is to make them comfortable with the concept and see its practical value.
Estimating Decimal Quotients: A Review
– Recap: Understanding Decimals
– Decimals represent parts of a whole, like 0.5 is half.
– Recap: Division Basics
– Division is splitting into equal parts or groups.
– Relating Decimals to Division
– Division can give results in decimal form.
– Estimating with Decimals
– Round decimals to estimate division answers.
|
Begin with a quick review of what decimals are, emphasizing their place value and how they represent fractions. Then, recap the basic division facts to ensure students are comfortable with division operations. Explain how decimals are related to division, particularly when dividing by numbers that don’t result in a whole number. Introduce the concept of estimating decimal quotients by rounding decimals to make division simpler and more approachable. Use examples to illustrate these concepts, such as dividing a dollar into quarters and estimating the result when dividing uneven numbers. Encourage students to practice rounding and estimating to build their confidence in working with decimals.
Estimation Basics: Decimal Quotients
– Understanding Estimation
– Estimation is finding a number close to the exact amount.
– The Purpose of Estimation
– Estimation helps us quickly find answers that are good enough for some purposes.
– Rounding Decimals
– To round, look at the number to the right of the decimal. If it’s 5 or more, round up.
– Estimating Decimal Quotients
– Use rounded numbers to estimate the quotient of decimal division.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of estimation, particularly when dealing with decimal quotients. Estimation is a valuable skill that allows for making quick and reasonably accurate calculations without needing the exact number. It’s especially useful in everyday situations where an approximate value is sufficient. Teach students how to round decimals to the nearest whole number by looking at the digit to the right of the decimal point. Emphasize that estimation is not about finding the precise answer but rather a close approximation that is easier to work with. Practice rounding a few decimal numbers as a class and then use those rounded numbers to estimate the results of some division problems.
Estimating Decimal Quotients
– Learn steps to estimate quotients
– Round decimals, then divide
– Example: Estimate 4.56 ÷ 0.92
– Round 4.56 to 5 and 0.92 to 1, then divide
– Use estimation to check answers
– After solving, compare with the estimate
– Understand estimation benefits
|
This slide introduces the concept of estimating decimal quotients as a way to quickly gauge the reasonableness of an answer. Start by explaining the steps to estimate: rounding the numbers to make division simpler, then performing the division. Use the example 4.56 ÷ 0.92 to show how to round each number and then estimate the quotient. Emphasize the importance of using estimation as a tool to check the accuracy of their actual division answers. Encourage students to practice with different decimal division problems and use estimation to verify their results. This skill will help them in checking their work and understanding the magnitude of their answers in real-world contexts.
Estimating Decimal Quotients: Practice
– Work through Example 1 together
– Estimate 3.49 divided by 1.13
Round to nearest whole number: 3 ÷ 1
– Work through Example 2 together
– Estimate 6.37 divided by 0.42
Round to nearest whole number: 6 ÷ 0.5
|
This slide is designed for a collaborative classroom activity where students practice estimating decimal quotients. Start with Example 1 by rounding the numbers to the nearest whole number to simplify the division. For 3.49 ÷ 1.13, round to 3 ÷ 1. Then, move to Example 2, using the same estimation technique. For 6.37 ÷ 0.42, round to 6 ÷ 0.5. Encourage students to explain their rounding choices and how it affects the estimate. This exercise will help students understand the concept of estimation and its usefulness in quickly solving division problems involving decimals without a calculator. Provide additional examples if time allows and encourage students to try estimating before calculating the exact answer.
Class Activity: Estimate the Quotient
– Pair up with a classmate
– Solve the estimation problems
– Use rounding to make the decimals easier to divide
– Record your estimated quotients
– Write down your estimates to compare later
– Share your answers with the class
– Discuss how you got your estimates and listen to others
|
This activity is designed to encourage collaboration and discussion among students as they practice estimating decimal quotients. Have the students pair up and provide them with a set of problems where they need to estimate the quotient of decimal numbers. Remind them to use rounding to simplify the decimals before dividing. After solving the problems, each pair should record their answers. Then, facilitate a class discussion where pairs share their estimated quotients and the methods they used to arrive at them. This will help students see different approaches to estimation and understand the concept better. Possible activity variations could include: 1) Estimating quotients using different rounding rules, 2) Comparing exact answers to estimated ones to see the difference, 3) Using estimation to check the reasonableness of exact calculations, 4) Timing the activity to add a fun challenge.
Estimating Decimal Quotients: Recap
– Remember estimation steps
Round the divisor and dividend, then divide.
– Understand estimation value
Estimation saves time and checks work.
– Homework: More practice
Solve additional problems to strengthen skills.
– Share your estimation strategies
|
As we conclude, remember the steps for estimating decimal quotients: round the numbers to make them easier to divide, and then perform the division. Emphasize the value of estimation in everyday life, such as in shopping or cooking, where exact amounts are not always necessary. For homework, students should practice estimation with a new set of problems to reinforce their skills. Encourage them to share their strategies with the class next time, fostering a collaborative learning environment. This will help them understand different approaches and find the best method that works for them.