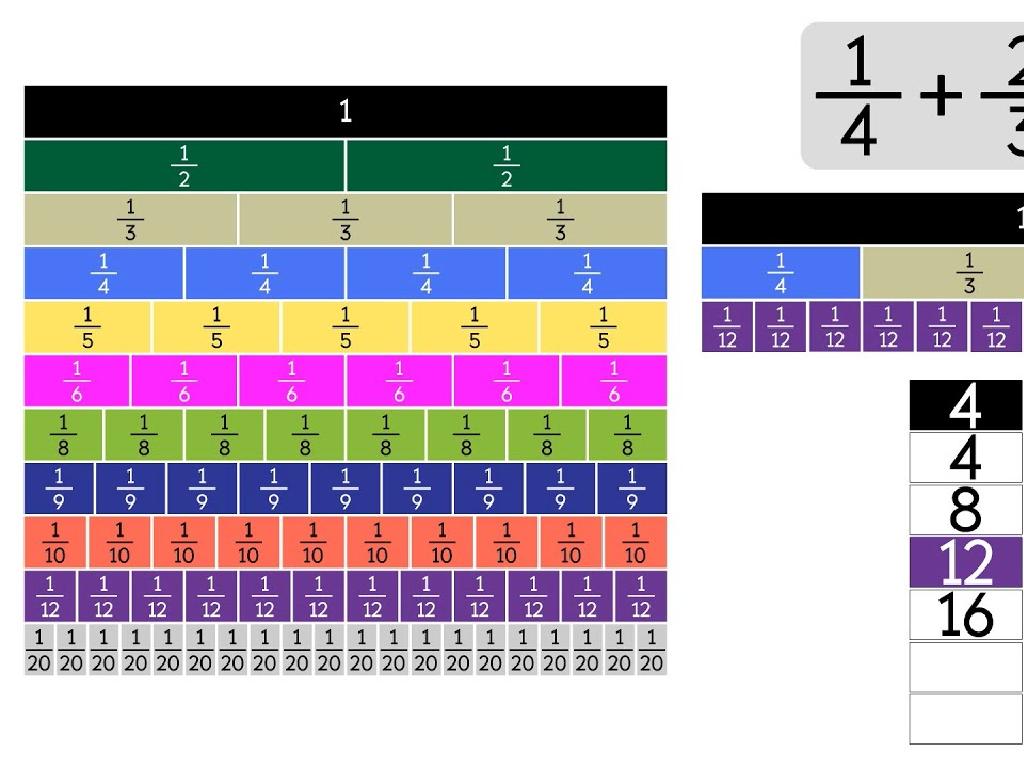
Divide By 2-Digit Numbers Using Models
Subject: Math
Grade: Fifth grade
Topic: Division
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Dividing by 2-Digit Numbers
– Division: Splitting equally
– Division is like sharing cookies equally among friends.
– Division with 2-digit divisors
– Instead of 1-digit, now we divide by numbers like 12 or 15.
– Why division matters
– Helps in real-life situations like splitting bills or sharing.
– Practice makes perfect
– We’ll do activities to get really good at it!
|
This slide introduces the concept of division as a method of splitting things into equal parts, with a focus on dividing by 2-digit numbers. Start by explaining division with simple examples, like sharing items equally. Emphasize the transition from dividing by 1-digit to 2-digit numbers, which is a new skill for fifth graders. Discuss the importance of division in everyday life, such as dividing a pizza among friends or splitting costs. Encourage students that practice will help them master this skill. Include interactive activities where students can practice dividing by 2-digit numbers using models, such as base-ten blocks or grid paper, to reinforce their understanding.
Quick Review: Division Concepts
– Understanding division
– Division is splitting into equal parts or groups
– Recall single-digit division
– Remember how we divide small numbers
– Solve example problems
– Let’s try 8 ÷ 2 and 15 ÷ 3 together
– Discuss equal sharing
|
This slide is aimed at refreshing the students’ memory on the basic concept of division as an act of splitting a number into equal parts. Start by explaining division in simple terms, such as sharing equally among friends. Then, prompt the students to recall division facts they already know, focusing on single-digit numbers to ensure they are comfortable with simpler problems before moving on to more complex ones. Work through the example problems as a class, and emphasize the idea of equal sharing to lay the groundwork for understanding division with larger numbers. This will prepare them for the next step, which is dividing by 2-digit numbers using models.
Dividing by 2-Digit Numbers Using Models
– Understanding 2-digit divisors
– A 2-digit number ranges from 10 to 99
– Represent division with models
– Use base-10 blocks or area models to visualize division
– Example: Divide 100 by 25
– How to divide 100 into 4 equal parts of 25
– Steps to model 2-digit division
– Draw the model, divide into tens and ones, subtract systematically
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of dividing by 2-digit numbers using visual models. Begin by explaining what 2-digit numbers are, emphasizing that they consist of tens and ones. Demonstrate how to use models such as base-10 blocks or area models to represent division problems. Provide a specific example, such as dividing 100 by 25, and walk through the steps using a model. This will help students understand the process of breaking down a larger number into smaller, more manageable parts. Encourage students to draw their own models and practice with different 2-digit divisors to solidify their understanding.
Dividing with Base-Ten Blocks
– Base-Ten Blocks for division
– Visualize division using blocks representing ones, tens, hundreds
– Steps for 2-digit division models
– Break down division into manageable steps using blocks
– Group activity: model building
Divide into groups, use blocks to solve a division problem
– Understanding division visually
|
This slide introduces the concept of using Base-Ten Blocks to model division, particularly when dividing by 2-digit numbers. Begin by explaining how each block type represents a different place value (ones, tens, hundreds) and can be used to represent the dividend. Then, demonstrate the step-by-step process of dividing a number using these models, ensuring to show how to deal with remainders. For the group activity, provide a set of division problems suitable for 2-digit division and have students work in small groups to build the division model and solve the problems. This hands-on activity will help solidify their understanding of the division process. Be prepared with several examples and ensure each group has enough blocks to work with. Encourage students to discuss their strategies and reasoning with the class after the activity.
Long Division with 2-Digit Divisors
– Understand DMSB steps
– Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down
– Apply DMSB to 2-digit divisors
– Same steps with larger numbers
– Work through 156 ÷ 12
– Let’s solve 156 ÷ 12 step by step
– Practice with similar problems
|
This slide introduces the long division method with 2-digit divisors, using the mnemonic ‘Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down’ (DMSB) to help students remember the steps. Start by explaining each step using simple examples. Then, apply the DMSB method to a 2-digit divisor problem, such as 156 ÷ 12, and solve it step by step on the board. Encourage students to follow along and solve the problem in their notebooks. After the example, provide additional problems for students to practice independently or in small groups to reinforce the concept. Remind them to check their work by multiplying the divisor by the quotient and adding the remainder to ensure it equals the dividend.
Practice Time: Division with 2-Digit Divisors
– Example: 156 ÷ 13
– How many times does 13 fit into 156?
– Example: 248 ÷ 16
– Can 16 go into 248 without remainder?
– Tips for accurate division
– Checking your work
– Use multiplication to verify your answers
|
This slide is designed for a hands-on practice session where students will apply their knowledge of division using 2-digit divisors. Start by working through the examples as a class, demonstrating the process step by step. For 156 ÷ 13, show how to break down the problem using long division or area models. Repeat the process with 248 ÷ 16, ensuring to highlight any differences in the approach due to the numbers involved. Emphasize the importance of checking work by multiplying the divisor by the quotient to see if it equals the dividend. Encourage students to ask questions and try these examples on their own, providing tips for common mistakes to avoid. This interactive approach helps solidify their understanding of the concept.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Division
– Remember to bring down the next digit
– Double-check multiplication and subtraction
– It s easy to multiply or subtract the wrong numbers. Always verify your calculations.
– Use estimation to check work
– Estimate the answer first to see if your division seems correct.
– Practice with different problems
– Try various exercises to become confident in division steps.
|
This slide addresses common errors made by fifth graders when learning to divide by 2-digit numbers. Emphasize the importance of bringing down the next digit in the division process, as skipping this step can lead to incorrect answers. Encourage students to always double-check their multiplication and subtraction to ensure accuracy. Introduce the concept of using estimation to verify the reasonableness of their answers. Provide a variety of practice problems for students to apply these strategies and reinforce their division skills. During class, work through examples together and discuss why each step is important to avoid these mistakes.
Class Activity: Division Relay
– Form teams for the relay
– Each member solves a step
– Work together to finish
– First team with correct answer wins!
|
This activity is designed to encourage teamwork and understanding of the division process. Divide the class into small groups, each group representing a team. Each team will work on a division problem involving a 2-digit divisor, but each member is responsible for only one step of the division process. This could include dividing, multiplying, subtracting, and bringing down the next digit. The first team to complete the problem correctly wins. Make sure to prepare different sets of problems for each team to prevent copying. This will help students understand the sequence of steps in division and the importance of each step in reaching the correct answer. It’s also a fun way to practice division with peers.
Homework and Wrap-Up: Division Mastery
– Complete tonight’s division homework
– Review using models for 2-digit divisors
– Use area models or base-ten blocks as practiced
– Write down any questions for next class
– Keep practicing and great job today!
|
For homework, students are tasked with completing a set of problems that require them to divide by 2-digit numbers using models. This will reinforce today’s lesson and help solidify their understanding. Encourage them to use area models or base-ten blocks to visualize the division process, as we’ve practiced in class. Remind students to write down any questions they come across while doing their homework to address in the next class. Congratulate the class on their hard work today and encourage them to keep practicing to improve their division skills. Possible activities for different students could include creating their own division word problems, using online math games to practice division, or working in small groups to solve complex division problems.