Money Banking And Central Banks
Subject: Economics
Grade: High school
Topic: Finance And Capital Markets
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
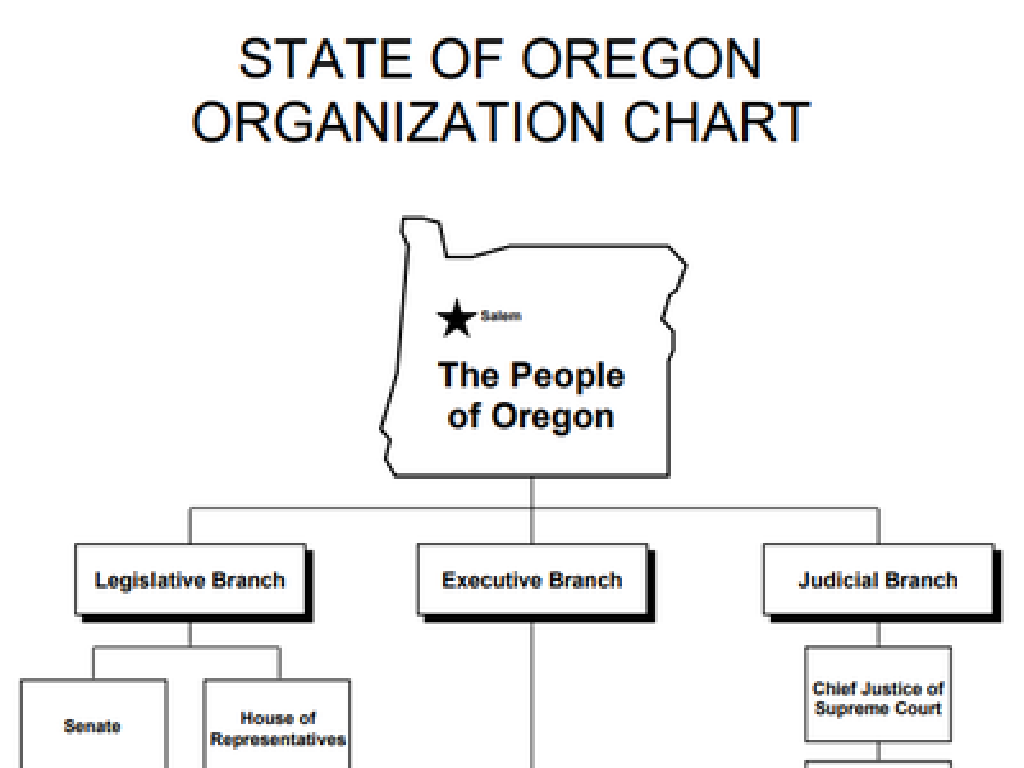
Introduction to Money, Banking, and Central Banks
– Role of money in the economy
– Medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account.
– Functions of a bank
– Banks manage deposits, provide loans, and facilitate transactions.
– Central banks and their role
– Central banks regulate money supply and maintain economic stability.
– Impact on financial stability
|
This slide introduces the fundamental concepts of money, banking, and the role of central banks in the economy. Money serves as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account, facilitating trade and economic activity. Banks are institutions that accept deposits, provide loans, and enable financial transactions, acting as the backbone of the financial system. Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, oversee the banking system, manage the nation’s money supply, and aim to ensure economic stability through monetary policy. Understanding these entities is crucial for comprehending the broader financial system and its impact on the economy. Encourage students to think about how these concepts affect their daily lives and the overall health of the country’s economy.
Understanding Money in Economics
– Define money and its functions
– Medium of exchange, store of value, unit of account
– Explore forms of money
– Commodity money, fiat money, and digital currency
– Characteristics of effective money
– Durability, portability, divisibility, uniformity, limited supply, acceptability
– Money’s role in the economy
|
This slide introduces the concept of money, which is a cornerstone of economic activity. Begin by defining money and discussing its three main functions: as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account. Then, delve into the different forms of money that have been used throughout history, including commodity money like gold, fiat money like dollar bills, and digital currencies such as Bitcoin. Highlight the six characteristics that make money effective: durability, portability, divisibility, uniformity, limited supply, and acceptability. Discuss why each characteristic is important and how they contribute to the overall utility of money in an economy. Encourage students to think critically about how the form and characteristics of money affect its function and value.
The Role of Banks in the Economy
– Banks as financial intermediaries
– Banks connect savers with borrowers, supporting economic activity.
– Services: Savings, Loans, Mortgages
– Banks offer accounts for saving money, lending for various needs, and investment opportunities.
– Understanding Interest Rates
– Interest rates are the cost of borrowing or the reward for saving.
– Impact of Rates on Economy
– Rates influence spending, saving, and inflation.
|
This slide aims to explain the fundamental role of banks in the economy and how they operate as intermediaries between savers and borrowers. Highlight the variety of services banks provide, including savings accounts, loans, mortgages, and investment options. Discuss how interest rates are determined and their dual role as a cost of borrowing and a reward for saving. Emphasize the broader impact of interest rates on the economy, affecting consumer spending, saving habits, and overall economic growth. Use examples like the effect of high-interest rates on mortgage payments or savings account yields to illustrate these concepts. Encourage students to think critically about how changes in interest rates might affect their personal financial decisions.
Central Banks and Monetary Policy
– Central Bank definition
– A nation’s primary financial institution, e.g., the Federal Reserve in the U.S.
– Key functions of a Central Bank
– Oversee monetary policy, regulate banks, ensure financial stability, manage inflation
– Monetary Policy tools
– Open Market Operations, setting the Discount Rate, and determining Reserve Requirements
– The Federal Reserve example
– The Fed serves as the central bank for the United States, implementing national monetary policy
|
This slide introduces the concept of a central bank and its role in the economy, using the Federal Reserve as a primary example. The central bank is crucial for implementing monetary policy, regulating the banking system, maintaining financial stability, and managing inflation. Students should understand the tools central banks use, such as Open Market Operations, which involve buying and selling government securities, adjusting the Discount Rate, which is the interest rate for banks borrowing from the central bank, and setting Reserve Requirements, which dictate the amount of funds banks must hold in reserve. The Federal Reserve is a practical example of a central bank that carries out these functions to influence the U.S. economy. Encourage students to think about how these actions can affect their daily lives, such as changes in interest rates affecting loan costs.
Central Banks’ Role in the Economy
– Central banks control interest rates
– Lower rates can boost borrowing and spending
– They regulate the money supply
– More money in circulation can lead to inflation
– Inflation vs. unemployment dynamics
– Known as the Phillips Curve relationship
– Case Study: 2008 Financial Crisis
– Central banks took unprecedented steps to stabilize markets
|
This slide aims to explain the pivotal role central banks play in influencing economic activity. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can either encourage or discourage borrowing and spending, which in turn affects economic growth. The money supply is another critical lever, with implications for inflation. Students should understand the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment, known as the Phillips Curve. The 2008 Financial Crisis provides a real-world example of how central banks can intervene in times of economic distress, using tools like lowering interest rates and quantitative easing to inject liquidity into the economy. Discuss the actions taken by the Federal Reserve during the crisis and their impact on the economy.
Global Perspective on Central Banks
– Compare world central banks
– How do the Fed, ECB, and BoJ differ in policy?
– Role of IMF and World Bank
– They provide financial stability and aid globally.
– International central bank cooperation
– They work together to manage global financial systems.
– Impact on global economy
|
This slide aims to provide students with a global perspective on how central banks operate in different countries and their collaborative efforts. Start by comparing the Federal Reserve (Fed), European Central Bank (ECB), and Bank of Japan (BoJ), focusing on their unique monetary policies and objectives. Discuss the role of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank in providing financial stability and assistance to countries in need. Highlight how central banks cooperate internationally, particularly during crises, to ensure a stable global financial system. This discussion will help students understand the interconnectedness of the world’s economies and the importance of international financial institutions.
Class Activity: Central Bank Simulation
– Form groups: Central Bank, Banks, Consumers
– Make decisions in economic scenarios
– Each group will respond to events like interest rate changes or loans
– Discuss the impact of your choices
– Consider how decisions affect the economy and other groups
– Reflect on the simulation outcomes
– What did you learn about the role of banks and consumers?
|
This activity is designed to give students a practical understanding of the roles and interactions between central banks, commercial banks, and consumers. Divide the class into three groups, each representing different sectors of the economy. Provide various economic scenarios such as a change in interest rates, a recession, or a boom. Each group will discuss and make decisions based on their role, then observe the consequences of their actions. After the role-play, lead a discussion to reflect on how each group’s decisions impacted the economy and each other. This will help students grasp the complexities of financial systems and the importance of policy decisions made by central banks.