Select Fractions Equivalent To Whole Numbers
Subject: Math
Grade: Third grade
Topic: Fractions Equivalent To Whole Numbers
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Fractions Equivalent to Whole Numbers
– What is a fraction?
– A fraction represents a part of a whole.
– Exploring equivalent fractions
– Fractions with different numbers that represent the same amount.
– Whole numbers as fractions
– A whole number can be written as a fraction with 1 as the denominator.
– Examples with common fractions
– 1 as 1/1, 2 as 2/1, 3 as 3/1, and so on.
|
This slide introduces the concept of fractions and their equivalence to whole numbers, which is a fundamental aspect of understanding fractions in third-grade math. Begin by explaining what a fraction is, using visual aids like pie charts or bar models to illustrate parts of a whole. Then, discuss equivalent fractions and show how different fractions can represent the same value. Highlight that every whole number can be expressed as a fraction with 1 in the denominator, providing examples such as 1 equal to 1/1, 2 equal to 2/1, and so on. Use simple, relatable examples to ensure students grasp the concept. Encourage students to think of other whole numbers and how they might be represented as fractions. This will prepare them for more complex operations involving fractions and whole numbers.
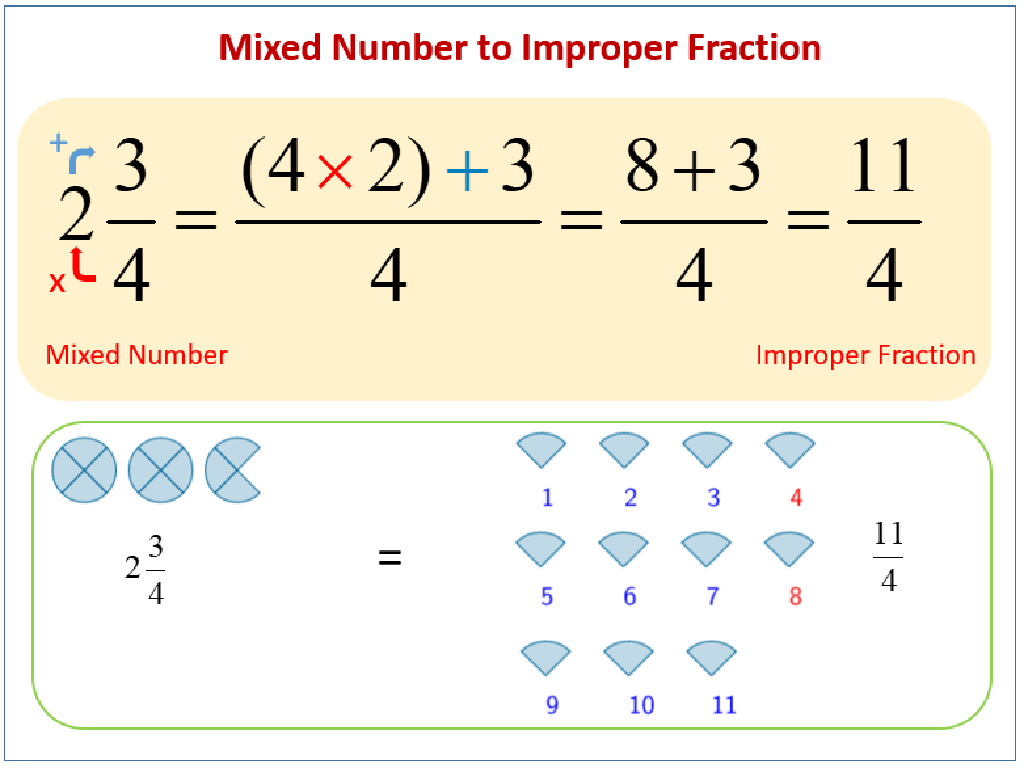
Understanding Fractions
– A fraction shows part of a whole
– Top number is the numerator
– It tells how many parts we have
– Bottom number is the denominator
– It tells how many equal parts the whole is divided into
– Example: 1/2 is one out of two parts
– Like half a pizza: 1/2 means 1 piece out of 2 total pieces
|
This slide introduces the concept of fractions to third-grade students. Begin by explaining that a fraction represents a part of a whole, something they see in everyday life, like a slice of pizza. The numerator, or top number, indicates how many parts of the whole we’re talking about. The denominator, or bottom number, shows into how many equal parts the whole is divided. Use the example of 1/2 to illustrate a common fraction, explaining that if a pizza is cut into two equal pieces, 1/2 means one of those pieces. Encourage students to think of other examples of halves in their environment to solidify their understanding.
Whole Numbers as Fractions
– Whole numbers as fractions
– Every whole number can be a fraction
– Numerator equals denominator
– The fraction’s top and bottom numbers are the same
– Example: 1 as a fraction
– 1 can be written as 1/1, which equals 1
|
This slide introduces the concept that every whole number can be expressed as a fraction. The key takeaway for the students is that when the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number) of a fraction are the same, it represents a whole number. For example, the number 1 is the same as the fraction 1/1. This concept is fundamental in understanding that fractions and whole numbers are part of the same number system. Encourage students to practice converting other whole numbers into fractions, such as writing 2 as 2/2, 3 as 3/3, and so on. This will help solidify their understanding of the relationship between whole numbers and fractions.
Understanding Equivalent Fractions
– What are equivalent fractions?
– Fractions with the same value, even if they look different
– Different fractions, same number
– Examples equivalent to 1
– Like 2/2, 3/3, 4/4 all equal to 1
– Practice finding equivalents
– Let’s find other fractions equal to whole numbers together
|
This slide introduces the concept of equivalent fractions to third-grade students. Start by explaining that equivalent fractions are different fractions that represent the same value. Emphasize that even though the numbers on the top and bottom of the fraction may change, the overall value can stay the same. Use simple, relatable examples such as 2/2, 3/3, and 4/4 to show that these all equal the whole number 1. Encourage students to think of fractions as parts of a whole and to visualize them to better understand equivalence. In the next class, practice with the students to find other equivalent fractions that equal whole numbers, reinforcing the concept through hands-on activities.
Finding Equivalent Fractions
– Multiply numerator & denominator
– Use the same number for both to find an equivalent fraction.
– Example: 1/1 becomes 2/2
– When you multiply 1/1 by 2, you get 2/2, which is equal to 1.
– Equivalent fractions equal the same
– Practice with different numbers
– Try multiplying 1/1 by 3 to get 3/3, and see it still equals 1.
|
This slide introduces the concept of equivalent fractions, emphasizing that multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same number results in a fraction equivalent to the original. Use the example of 1/1 multiplied by 2 to get 2/2 to illustrate that the value remains 1, reinforcing the concept that equivalent fractions represent the same value. Encourage students to practice with different numbers to solidify their understanding. For instance, multiplying 1/1 by 3 to get 3/3 or by 4 to get 4/4, and so on, showing that these fractions are all equivalent to the whole number 1. This activity will help students recognize patterns in equivalent fractions and understand their relationship to whole numbers.
Practice Time: Equivalent Fractions to Whole Numbers
– Understand equivalent fractions
– Whole number 2 as a fraction
– 2 can be written as 2/1, which is a fraction
– Multiplying numerator & denominator
– Multiply top and bottom by the same number
– Example: 2/2 multiplied by 2
– 2/2 times 2 equals 4/4, which is also 2
|
This slide is for a class activity where students practice finding fractions equivalent to whole numbers. Start by explaining that a whole number can be expressed as a fraction by using 1 as the denominator. Then, demonstrate that multiplying the numerator and denominator by the same number gives an equivalent fraction. Use the example of 2/2 multiplied by 2 to show that 4/4 is also equivalent to the whole number 2. For the activity, have students come up with other numbers to multiply the numerator and denominator by, such as 3, 4, or 5, and see what equivalent fractions they can find for the number 2. Encourage them to explore with different whole numbers as well.
Class Activity: Fraction Match
– Match whole numbers to fractions
– Find fractions that equal numbers like 1, 2, 3
– Use fraction strips for help
– Fraction strips can show how many parts make a whole
– Share your matches with the class
– Discuss with friends how you found your answers
|
This activity is designed to help students visually understand the concept of equivalent fractions and whole numbers. Provide each student with a set of fraction strips that they can manipulate to match whole numbers to their equivalent fractions. For example, 1 can be matched with 1/1, 2 with 2/1 or 4/2, and so on. Encourage students to use the strips to see how many equal parts make up a whole number. After they find matches, ask them to share their findings with the class to reinforce their understanding. Possible variations of the activity could include pairing students to find matches together, creating a fraction match game with a timer, or having students create their own fraction strips from paper.
Wrapping Up: Fractions Equivalent to Whole Numbers
– Review of equivalent fractions
– Homework: 3 fractions for the number 3
– Examples: 3/1, 6/2, 9/3 are all equal to 3
– Draw the equivalent fractions
– Use pie charts or bar models to visualize
– Next class: Fractions less than 1
|
As we conclude today’s lesson, remind the students about the concept of equivalent fractions and how they can represent the same value as whole numbers. For homework, students should find three different fractions that are equivalent to the whole number 3 and represent them visually. This could be through drawing pie charts or bar models to show how the fractions are equal to a whole. In the next class, we will shift our focus to understanding fractions that represent values less than 1, building on the foundation of equivalent fractions. Encourage students to think creatively about how to draw their fractions and to check their work by ensuring each fraction simplifies to the whole number 3.

/convergence_divergence_history.png)