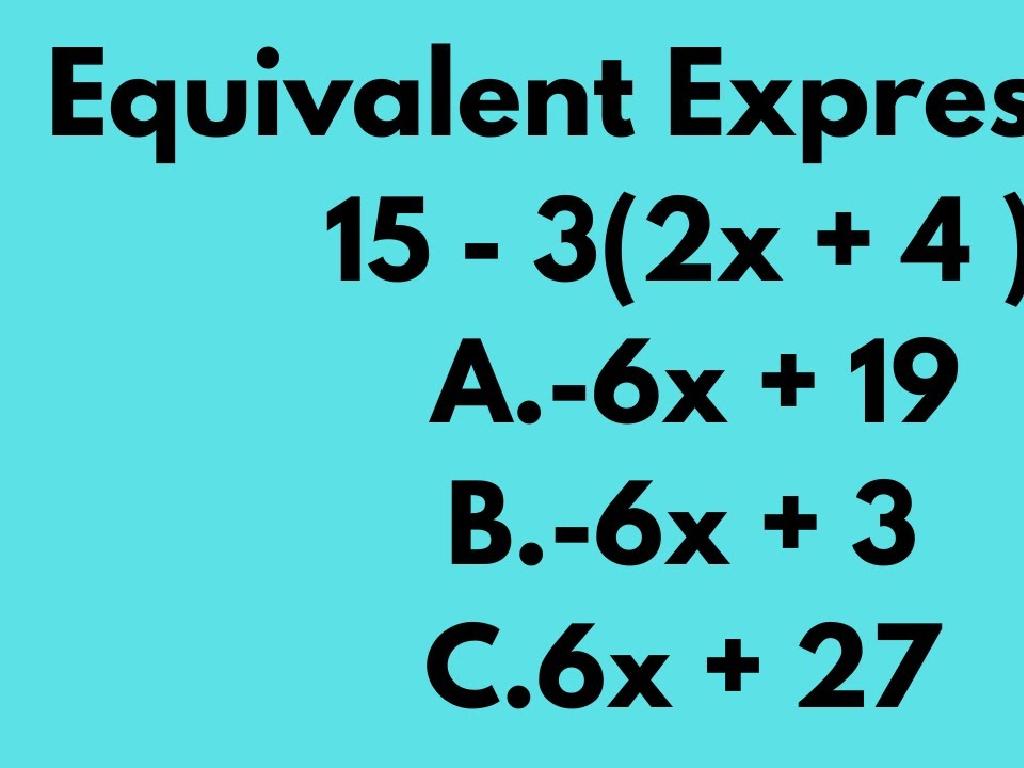Graph A Line From An Equation In Standard Form
Subject: Math
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: Linear Equations
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Graphing Lines from Standard Form Equations
– What is standard form?
– Standard form: Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers
– Steps to graph a line
– Plot points, find intercepts, draw the line
– Real-life applications
– Used in budgeting, planning, construction
– Practice problems
|
Begin with explaining the standard form of a linear equation, emphasizing the structure and the integers involved. Demonstrate the process of graphing a line by finding x and y intercepts from the standard form equation. Discuss how linear equations apply to various real-life scenarios such as budgeting finances, planning trips, or even in construction and engineering. Conclude with practice problems to solidify the students’ understanding and to give them hands-on experience with graphing from standard form. Encourage students to think of other areas where linear equations are applicable.
Graphing Lines from Standard Form Equations
– Define Standard Form
– An equation Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers
– Standard Form Equation
– Example: 3x + 2y = 6
– Characteristics of Standard Form
– A and B are not both zero; A should be positive
– Standard Form Examples
– Graph 2x – 3y = 6 and 5x + y = 10
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of standard form for linear equations, which is a way of writing equations that allows for easy identification of the x and y intercepts. Emphasize that in standard form, A, B, and C are integers, and A should be a non-negative integer. Discuss the importance of the standard form in graphing lines and solving systems of equations. Provide examples of standard form equations and demonstrate how to graph them by finding the intercepts. Encourage students to practice converting equations to standard form and graphing them.
Converting to Standard Form
– Rearrange equations into standard form
– Standard form: Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers
– Practice: y = 2x + 3 to standard form
– Move variables to one side, constants to the other
– Understand roles of A, B, and C
– A, B represent slope factors; C is y-intercept
– Why standard form is useful
|
This slide introduces the concept of standard form and its significance in graphing linear equations. Start by explaining the structure of the standard form equation, Ax + By = C, and the requirement for A, B, and C to be integers. Use the practice problem to demonstrate how to rearrange y = 2x + 3 into standard form by moving terms across the equals sign. Emphasize the importance of A and B as they relate to the slope of the line, and C as the point where the line crosses the y-axis. Conclude by discussing why expressing equations in standard form is beneficial for analyzing and graphing linear relationships. Provide additional practice problems for students to solidify their understanding.
Plotting a Line from Standard Form
– Find points from standard form
Use Ax + By = C to find points; set y=0 for x-intercept, x=0 for y-intercept
– Determine X and Y intercepts
X-intercept is where line crosses x-axis, Y-intercept is where line crosses y-axis
– Plot intercepts on the graph
Mark the intercepts on graph’s axes
– Draw the line through intercepts
Connect the intercepts with a ruler for an accurate line
|
This slide is aimed at teaching students how to graph a line from an equation in standard form. Start by explaining the standard form of a linear equation (Ax + By = C). Show how to find specific points by substituting zero for one variable at a time to find the intercepts. Emphasize the importance of the x-intercept (where the line crosses the x-axis) and the y-intercept (where the line crosses the y-axis). Demonstrate how to plot these points on a coordinate graph and then connect them to form the line. Encourage students to practice this method with different equations to become comfortable with the process.
Graphing a Line from Standard Form
– Plotting points on the grid
– Use x and y values to locate points
– Understanding slope importance
– Slope determines the line’s steepness and direction
– Drawing lines with precision
– Use a ruler to connect dots for a straight line
– Checking line accuracy
– Verify the line matches the equation’s predictions
|
This slide is aimed at teaching students how to graph a line from an equation in standard form. Start by explaining how to find x and y intercepts from the equation and plot these points on the coordinate grid. Emphasize the role of slope as the rate of change between the points and how it affects the line’s direction and steepness. Demonstrate the use of a ruler to ensure the line drawn is straight, which is crucial for accurate representation. Finally, encourage students to check their graph against the equation to confirm its accuracy. Provide examples and practice problems for students to apply these concepts.
Real-World Applications of Linear Equations
– Linear equations model real life
– Example: Budgeting on fixed income
– If you earn $50 weekly, how to allocate for expenses?
– Graph interpretation in daily life
– Understand how graphs translate to decisions
– Activity: Create your own budget graph
– Use a standard form equation to plan spending
|
This slide aims to show students how linear equations are not just theoretical concepts but are actually used in everyday life, such as in budgeting with a fixed income. Provide an example where a fixed weekly income needs to be allocated to different expenses, and how a graph can help visualize and plan spending. Encourage students to interpret graphs by relating the x-axis to weeks and the y-axis to dollars spent. For the activity, guide students to create their own budget graph using a linear equation in standard form, considering their weekly allowance and expected expenses. This will help them understand the practicality of linear equations and enhance their problem-solving skills.
Class Activity: Graphing Challenge
– Pair up and solve equations
– Graph equations on poster paper
– Present your graph to class
– Explain your solution process
– Share steps taken to graph the line from the standard form equation
|
This activity is designed to promote collaborative learning and hands-on practice with graphing lines from standard form equations. Students should be paired up to encourage teamwork. Provide each pair with a set of standard form equations to solve. Once they have solved the equations, they will graph their lines on poster paper, which will later be used to present their findings to the class. Encourage each group to discuss their approach to solving the equations and how they graphed the line. As a teacher, prepare to guide students through the process, offering hints and strategies as needed. Possible activities include graphing lines with different slopes, y-intercepts, or discussing how changes in the equation affect the graph’s position. This will help students understand the relationship between the algebraic equation and its graphical representation.
Conclusion: Graphing Lines & Homework
– Recap: Graphing from Standard Form
– Homework: Graph 3 Equations
– Use skills learned to graph Ax + By = C
– Next Class: Slope-Intercept Form
– We’ll learn another method to graph lines
– Practice reinforces understanding
|
As we conclude today’s lesson on graphing lines from standard form equations, ensure students are comfortable with the process of converting equations and plotting them on a graph. For homework, students should graph three different linear equations from standard form to reinforce their understanding. In our next class, we will explore the slope-intercept form, which is another technique for graphing linear equations. Encourage students to practice diligently as this will solidify their grasp of the concepts and prepare them for the next lesson. Provide examples of standard form equations for homework and remind students to label their graphs clearly.