Feudal Europe
Subject: Social studies
Grade: Sixth grade
Topic: Medieval Europe
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Exploring Feudal Europe
– Medieval Europe overview
– A period marked by castles, knights, and the manorial system.
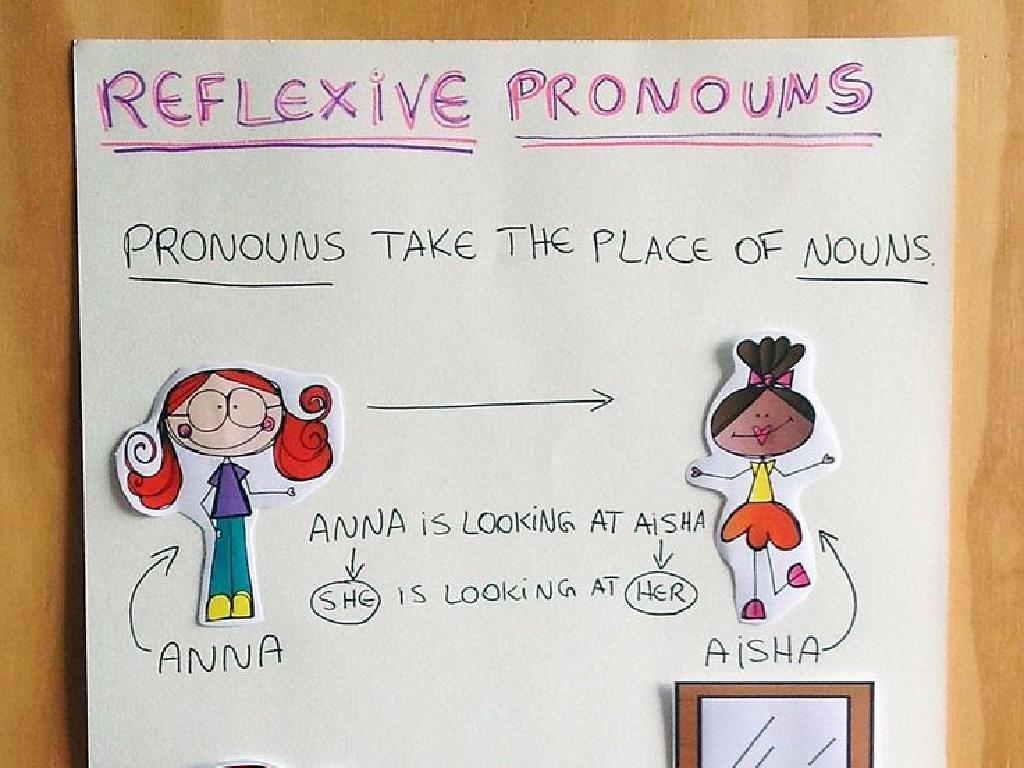
– Feudalism explained
– A system where land was exchanged for service and protection.
– Significance of studying Feudal Europe
– Learning about Feudal Europe helps us understand historical societal structures.
– Insights into social hierarchy
– Feudalism created a strict social order with kings, nobles, knights, and peasants.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of Feudal Europe, a significant era in Medieval history. Begin with a brief overview of Medieval Europe, setting the stage for the emergence of feudalism. Explain feudalism as a system of mutual obligations, where lords owned land but granted it to vassals (nobles and knights) in exchange for military service, while peasants worked the land for protection and sustenance. Emphasize the importance of studying Feudal Europe to understand the evolution of social and political structures and how they have shaped modern society. Highlight the rigid social hierarchy that characterized the period, which can be a precursor to discussions on social mobility and class systems.
Understanding Feudalism in Medieval Europe
– Feudalism defined
– A social system in Medieval Europe where people worked and fought for nobles in return for protection and land.
– Roles within Feudal society
– Kings ruled the land, Lords managed estates, Knights provided military service, and Serfs worked the land.
– Land in exchange for service
– Lords granted land to Knights in return for military service and protection.
– Feudal hierarchy and obligations
|
Feudalism was the dominant social system in Medieval Europe. It was based on the exchange of land for military and other services. Kings were at the top, owning all the land, which they granted to Lords (nobles). In return, Lords promised loyalty and military support. Knights, given land by Lords, served as soldiers. Serfs, bound to the land, worked for the Lords and Knights, receiving protection and a place to live. This system created a clear hierarchy and mutual obligations that structured medieval society. Discuss the concept of mutual obligation and how this system influenced every aspect of life during the period. Encourage students to think about the pros and cons of such a system.
Daily Life in Feudal Europe
– Compare lord and serf lifestyles
– Lords owned land, serfs worked it
– Explore the manorial system
– Manors were self-contained with farms, homes, and churches
– Understand women’s roles
– Women managed households or worked on farms
– Discuss daily activities and responsibilities
|
This slide aims to give students a glimpse into the stark contrasts between the lives of lords and serfs in Feudal Europe. Lords were the landowners and rulers of the manor, while serfs were peasants bound to the land, working it to sustain themselves and their lord. The manorial system was the economic and social structure of the time, with each manor acting as a self-sufficient community. Women, although limited in rights, played vital roles in both noble and peasant families, managing households or laboring in fields. Encourage students to think about how different their lives would be in a feudal society and to consider the implications of a class-based system on daily life.
Feudalism and the Economy
– Agriculture: economy’s foundation
– Farming was key for food and trade.
– Medieval trade and commerce
– Markets and fairs were trade hubs.
– Feudalism’s impact on economy
– Feudalism shaped wealth distribution.
– Economic roles in feudal society
– Lords, vassals, and serfs had specific economic duties.
|
This slide explores the economic structure of Feudal Europe, emphasizing agriculture as the cornerstone of the medieval economy. Students should understand that the majority of people were involved in farming, which provided the food supply and raw materials for trade. Highlight the role of local markets and fairs as centers for trade and commerce. Discuss how the feudal system, with its hierarchy of lords, vassals, and serfs, influenced economic development and the distribution of wealth. Explain the economic responsibilities of each class within the feudal system. Encourage students to think about how this system compares to our modern economy and the roles different people play in it.
The Decline of Feudal Europe
– Factors leading to feudalism’s fall
– Political changes, wars, and peasant revolts
– The Black Death’s devastating effects
– Plague reduced population, causing labor shortages
– Emergence of towns and middle class
– Trade increased, towns grew, and a new class emerged
– Economic and social shifts
|
This slide explores the reasons behind the decline of the feudal system in Europe. Key factors include political changes, such as the strengthening of monarchies, wars that drained resources, and peasant revolts demanding more rights. The Black Death, a catastrophic plague, significantly reduced the population, leading to labor shortages and increased wages. This, in turn, weakened the manorial system. The growth of trade led to the rise of towns and a burgeoning middle class, which shifted the economic balance away from the feudal lords. These economic and social changes paved the way for the end of feudalism and the beginning of a more modern Europe. Encourage students to think about how these factors interplayed to bring about such a significant change in society.
Feudal Europe: A Lasting Legacy
– Feudalism’s impact on Europe
– Feudalism structured society and land ownership
– Influence on modern politics
– Elements seen in current government structures
– Medieval culture’s enduring legacy
– Traditions, art, and architecture still appreciated
– Understanding feudalism’s role today
|
This slide aims to explore the enduring impact of feudalism on contemporary Europe. Feudalism, with its hierarchical structure of land ownership and societal roles, laid the groundwork for modern property laws and social classes. Its influence extends to modern political systems, where vestiges of feudal governance can be seen in certain constitutional frameworks and legal systems. The cultural aspects of the medieval period, including art, literature, and architecture, continue to be celebrated and studied for their historical significance and beauty. Students should understand that the legacy of feudal Europe is not just a relic of the past but a living influence that continues to shape our world in various ways.
Class Activity: Build Your Own Feudal Society
– Split into groups for activity
– Each group designs a feudal society
– Assign roles within your society
– Think about lords, knights, peasants
– Prepare a presentation of your society
– Include a manor, fields, and homes in your layout
|
This interactive class activity is designed to help students understand the structure and roles within a feudal society during Medieval Europe. Divide the class into small groups and provide them with materials to create their own feudal society. Each group should discuss and assign roles such as lords, knights, and peasants, and design a manor layout that includes essential features like the lord’s home, peasant cottages, fields for farming, and areas for animals. Encourage creativity and ensure that each group understands the hierarchy and the daily life in their society. After the activity, each group will present their society to the class, explaining the roles and the layout they’ve designed. This will help students to visualize and better grasp the concept of feudalism. As a teacher, be ready to provide guidance and historical facts to enrich their understanding.