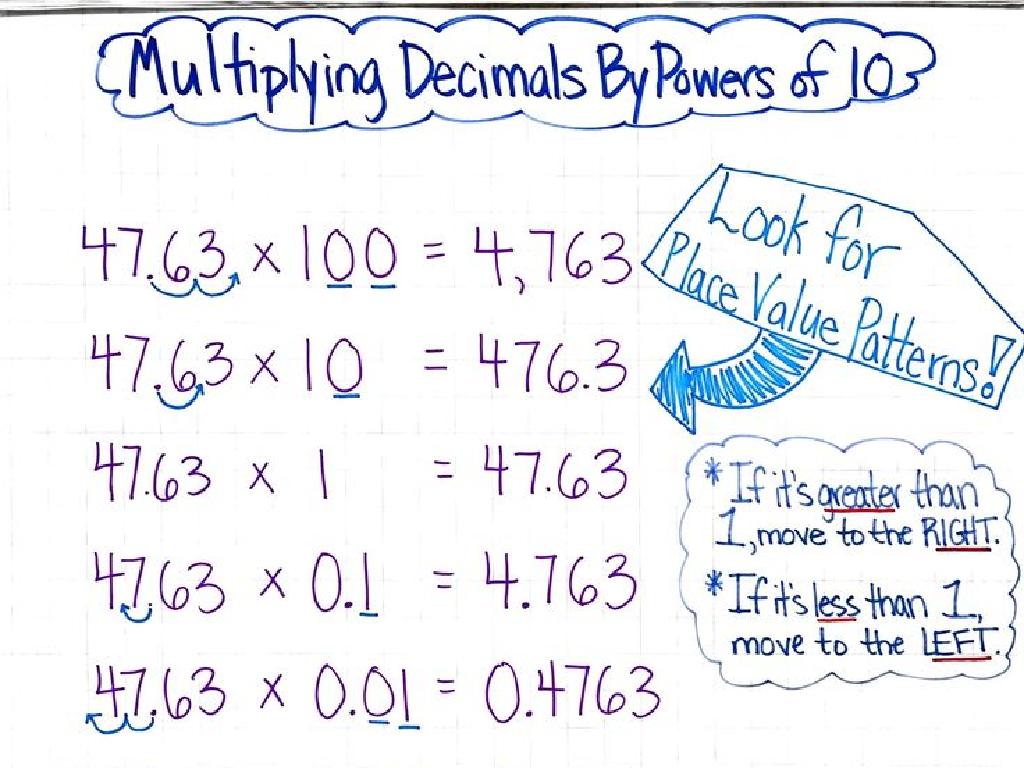
Multiply Two Decimals: Where Does The Decimal Point Go?
Subject: Math
Grade: Fifth grade
Topic: Multiply Decimals
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Multiplying Two Decimals: Getting Started
– Grasping the concept of decimals
– Decimals represent parts of a whole, like money.
– Understanding multiplication
– Multiplication combines equal groups; 3 x 4 means 3 groups of 4.
– Preview: Decimal multiplication
– When we multiply decimals, we combine parts of numbers.
– Locating the decimal point
– After multiplying, count total decimal places from both numbers for placement.
|
This slide introduces the concept of multiplying decimals, starting with a basic understanding of what decimals are and how they represent fractions of a whole, which is relatable to everyday concepts like money. Then, it explains the fundamental idea of multiplication as combining equal groups. The preview of decimal multiplication sets the stage for the lesson, emphasizing the importance of understanding where the decimal point goes in the product. The slide prepares students for the detailed process of multiplying two decimals, ensuring they grasp the initial concepts before moving on to examples and practice problems. Encourage students to think of decimals in terms of money to make the concept more tangible.
Understanding Decimal Places
– What is a decimal point?
– Decimal places: tenths, hundredths
– Places right of a decimal: first is tenths, then hundredths, etc.
– Counting decimal places
– Add up places from both numbers to find the new decimal point position
– Practice with examples
– Let’s identify decimal places in 0.5 x 0.25
|
This slide is aimed at reviewing the concept of decimal places, which is crucial for understanding how to multiply decimals. Begin by explaining the decimal point as a separator between whole numbers and fractional parts. Emphasize the names of the places to the right of the decimal point and how each place represents a power of ten. Engage the students in counting decimal places in given numbers to ensure they understand how to determine the position of the decimal point in the product. Use examples like 0.5 (one decimal place) multiplied by 0.25 (two decimal places) to illustrate the process, resulting in a product with three decimal places. Encourage students to practice with additional examples and provide immediate feedback to solidify their understanding.
Multiplying Whole Numbers
– Review multiplication facts
– Recall times tables up to 10×10
– Steps to multiply whole numbers
– Multiply numbers step by step
– Practice multiplication
– Solve practice problems in class
– Understand place value
– Recognize the value of each digit
|
This slide is aimed at reinforcing the students’ understanding of basic multiplication before introducing the concept of multiplying decimals. Start with a quick review of multiplication facts, ensuring that students are comfortable with times tables up to 10×10. Then, explain the process of multiplying whole numbers, emphasizing the importance of aligning the numbers by their place value. Provide a set of practice problems for students to work on, either individually or in groups, to apply what they’ve learned. Highlight the significance of place value, as it will be crucial when they move on to multiplying decimals. This foundational knowledge is essential for understanding where the decimal point goes in the product of two decimals.
Multiplying Decimals: Placing the Decimal Point
– Multiplying decimals vs. whole numbers
– Decimals require decimal point placement unlike whole numbers.
– Align numbers vertically for clarity
– Proper alignment ensures accurate multiplication.
– Example: Single decimal multiplication
– Multiply 0.5 (1/2) by 4 to get 2.0, showing decimal in product.
– Practice with different decimal places
– Try multiplying 0.3 by 0.2 to understand two-decimal multiplication.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of multiplying decimals and highlights the differences from multiplying whole numbers, particularly the importance of decimal point placement. Emphasize the need for careful alignment of numbers to avoid errors. Use the example of multiplying a single decimal by a whole number to demonstrate the process, and then encourage students to practice with problems involving different numbers of decimal places to solidify their understanding. Provide additional examples and practice problems to ensure students are comfortable with the concept.
Multiplying Two Decimals
– Steps to multiply decimals
– Multiply as whole numbers, ignore the decimal
– Placing the decimal point
– Count total decimal places in both numbers
– Example: Multiply 0.3 by 0.4
– Result is 0.12, with decimal after 2 places
|
This slide introduces the process of multiplying two decimal numbers, focusing on the correct placement of the decimal point in the product. Begin by explaining that the multiplication process is similar to that of whole numbers, where students can temporarily ignore the decimal points. Emphasize the importance of counting the total number of decimal places in both factors to determine where the decimal point will be placed in the answer. Use the example of multiplying 0.3 by 0.4 to illustrate the concept, showing that since each number has one decimal place, the product must have two decimal places, resulting in 0.12. Encourage students to practice with additional examples and to verify their answers by estimating the product.
Multiplying Decimals: Practice Problems
– Multiply: 0.25 x 0.6
– How many places are there after the decimal in the answer?
– Multiply: 0.75 x 0.4
– Let’s find the product and the position of the decimal point.
|
This slide presents two practice problems to help students understand the process of multiplying decimals and determining the correct placement of the decimal point in the product. For the first problem, guide the students to multiply as if there are no decimals and then count the total number of decimal places in both factors (0.25 has two and 0.6 has one, so three in total). The product should then have three decimal places. Similarly, for the second problem, there are two decimal places in each factor, so the product should have four decimal places. Encourage students to use grid paper or place value charts if they need help visualizing the decimal placement. After solving, discuss the importance of accuracy in decimal placement and how it affects the value of the answer.
Multiplying Decimals: Finding the Right Spot for the Decimal
– First, ignore the decimal points
– Multiply the numbers as if they’re whole
– Count decimal places in both numbers
– Add up the decimal places from both numbers
– Place the decimal in your answer
– The sum of decimal places guides where to put the decimal
|
When teaching students to multiply decimals, a helpful strategy is to initially ignore the decimal points and multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers. This simplifies the process and prevents confusion. After obtaining the product, instruct students to count the total number of decimal places in the original numbers. This count is crucial as it determines where the decimal point will be placed in the answer. For example, if multiplying 1.2 (one decimal place) by 3.45 (two decimal places), the answer should have three decimal places. Practice this technique with several examples and ensure students understand the importance of accurately placing the decimal point to get the correct answer.
Class Activity: Decimal Multiplication
– Pair up for multiplication practice
– Solve decimal problems together
– Use grid paper to align decimal points
– Discuss methods and answers
– Explain your strategy to your partner
– Complete the activity worksheet
– Worksheet has problems with different decimal places
|
This slide introduces a collaborative class activity focused on multiplying decimals. Students will pair up to work through a series of decimal multiplication problems, which will help them understand where the decimal point goes in the product. Encourage students to use grid paper to keep their work neat and align decimal points correctly. After solving the problems, they should discuss their methods and answers with their partner and then share their strategies with the class to foster a collaborative learning environment. The activity worksheet should contain problems of varying difficulty, including different numbers of decimal places, to challenge all students. As a teacher, circulate the room to offer guidance and ensure that each pair understands the concept. Possible activities could include creating their own decimal multiplication problems, peer-teaching a problem they’ve solved, or using manipulatives to represent decimal multiplication visually.
Conclusion: Multiplying Decimals
– Recap: Multiplying two decimals
– We learned how to find the product of decimal numbers.
– Importance of decimal placement
– Correct decimal placement ensures accurate calculations in real-world scenarios.
– Homework: Practice worksheet
– Complete the worksheet to reinforce today’s lesson.
|
Today’s lesson focused on multiplying two decimal numbers and understanding the correct placement of the decimal point in the product. This skill is crucial as it applies to real-life situations such as handling money, measuring quantities, and interpreting data accurately. For homework, students are assigned a practice worksheet to further solidify their understanding of decimal multiplication. The worksheet should include a variety of problems, some of which require students to estimate the position of the decimal point before multiplying to check their understanding. Encourage students to review their notes and use the multiplication steps discussed in class to solve the problems.