Evaluate Claims About Natural Resource Use: Groundwater
Subject: Science
Grade: Seventh grade
Topic: Natural Resources And Human Impacts
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
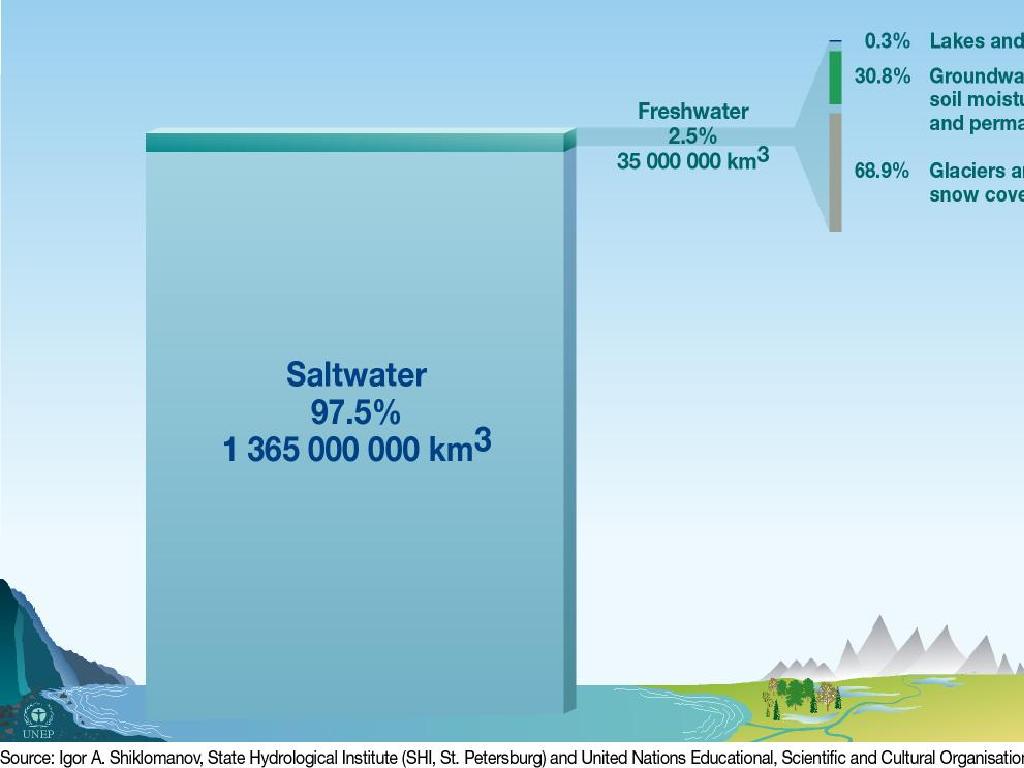
Groundwater: Earth’s Hidden Treasure
– Earth’s natural resources overview
– Defining natural resources
– Resources naturally occurring on Earth like water, air, and minerals
– Groundwater as a vital resource
– Underground water that sustains ecosystems and human use
– Human impact on groundwater
– Overuse and pollution can deplete and contaminate groundwater
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of natural resources, with a specific focus on groundwater. Begin by discussing the variety of natural resources our planet provides, such as water, air, minerals, and oil. Clarify that natural resources are materials or substances that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain or sustenance. Emphasize the importance of groundwater, which is water found beneath the Earth’s surface that fills pores and fractures in rocks and sediments. Highlight how groundwater is crucial for both ecosystems and human consumption, being a source for wells and aquifers. Discuss the human impact on groundwater, including the risks of over-extraction and pollution, which can lead to scarcity and health issues. Encourage students to think about how their actions can affect the availability and quality of groundwater.
Groundwater: The Water Beneath Our Feet
– Understanding groundwater
– Water stored in the Earth’s subsurface soil and rocks.
– Formation of groundwater
– Rain or snow infiltrates the ground and fills the porous spaces in soil, sand, and rocks.
– Groundwater in the water cycle
– Groundwater moves through the water cycle, contributing to springs, rivers, and lakes.
– Groundwater’s ecological role
– It supports ecosystems and human needs by providing water for drinking, irrigation, and industry.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of groundwater, a critical natural resource that is often overlooked. Groundwater is the water found underground in the cracks and spaces in soil, sand, and rock. It is a major part of the water cycle, as it feeds into surface water sources like rivers and lakes and is replenished by precipitation. Groundwater plays a vital role in maintaining ecosystems and is a key source of water for agricultural, industrial, and personal use. Students should understand how groundwater is formed, its part in the water cycle, and its importance to life on Earth. Encourage them to think about how human activities can impact groundwater quality and availability.
The Importance of Groundwater
– Essential for drinking
– Groundwater provides safe, clean water for humans and animals.
– Vital for agriculture
– Irrigation systems rely on groundwater to grow crops.
– Used in industry
– Factories use groundwater in manufacturing and cooling processes.
– Supports ecosystems
– Wetlands and natural habitats depend on groundwater.
|
Groundwater is a critical natural resource that serves multiple purposes. It is a primary source of drinking water for both people and animals, ensuring health and survival. In agriculture, groundwater is used extensively for irrigation, making it a backbone of food production. Industrial uses include its application in various manufacturing processes, as well as in cooling systems for machinery. Moreover, groundwater plays a crucial role in maintaining natural ecosystems, such as wetlands, which support biodiversity. It’s important for students to understand the diverse applications of groundwater and the need for sustainable management to protect this vital resource.
Evaluating Claims About Groundwater Use
– Understanding what a claim is
– A claim is a statement or assertion about something, often about the effects of human actions on groundwater.
– Steps to evaluate claim validity
– To judge if a claim is valid, check the source, the evidence presented, and the logic used.
– Analyzing evidence and reasoning
– Evidence includes facts, data, or research; reasoning is how evidence is connected to the claim.
– Critical thinking in claim assessment
– Think critically about the claim’s implications and the quality of its justification.
|
This slide aims to teach students how to critically evaluate claims, particularly those related to the use of natural resources like groundwater. Start by defining a claim and then guide students through the process of evaluating its validity by considering the source of the claim, the evidence supporting it, and the reasoning behind it. Emphasize the importance of critical thinking and encourage students to question the reliability of the evidence and the soundness of the arguments presented. Provide examples of claims about groundwater use and work through the evaluation process together. This will help students develop the skills to make informed opinions about environmental issues.
Evaluating Groundwater Use
– Common claims about groundwater
– Groundwater is often believed to be a limitless resource.
– Effects of overusing groundwater
– Overuse can lead to depletion and environmental issues.
– Is groundwater use sustainable?
– Considering the recharge rate, continuous use may not be viable.
– Strategies for responsible use
– Conservation methods and regulated usage can help.
|
This slide aims to educate students on the critical nature of groundwater as a resource and the common misconceptions about its abundance. It’s essential to discuss the consequences of overusing groundwater, such as lowered water tables and reduced water quality, which can lead to environmental and economic problems. Students should understand that groundwater sustainability is a complex issue, dependent on factors like recharge rates and human consumption patterns. The class will explore whether our current use of groundwater can continue without causing long-term damage. Finally, we’ll discuss practical strategies for responsible groundwater use, emphasizing the importance of conservation and regulation to ensure availability for future generations.
Groundwater Use and Management
– Real-world groundwater usage
– How is groundwater used globally for agriculture, industry, and drinking?
– Sustainable use success stories
– Examples like San Antonio, Texas, using aquifer storage and recovery
– Effects of poor management
– Overuse can lead to sinkholes, contamination, and scarcity
– Balancing use and conservation
|
This slide examines the importance of groundwater as a natural resource and the impact of human activity on its sustainability. Students will explore how groundwater is utilized around the world, including for agriculture, industrial processes, and as a primary source of drinking water. Highlight success stories such as San Antonio’s effective aquifer management to inspire sustainable practices. Discuss the negative consequences of mismanagement, like depletion and pollution, which can lead to environmental and social issues. Emphasize the need for careful planning and regulation to ensure a balance between use and conservation of groundwater resources.
Group Activity: Evaluating Groundwater Claims
– Break into small groups
– Review your assigned claim about groundwater
– Consider the source, evidence, and logic of the claim
– Discuss the validity of the claim
– Use critical thinking to assess the claim’s credibility
– Prepare to present your conclusions
|
This group activity is designed to foster collaboration and critical thinking among students as they evaluate claims about groundwater use. Each group will receive a different claim related to groundwater, such as its availability, pollution, or management. Students should consider the reliability of the source, the evidence provided, and the reasoning behind the claim. After thorough discussion, each group will prepare a short presentation summarizing their assessment of the claim’s validity. As a teacher, facilitate the activity by ensuring each group understands their task, providing guidance on how to evaluate claims, and helping them prepare to share their findings with the class. Possible claims for evaluation could include the sustainability of groundwater extraction, the impact of agriculture on groundwater quality, or the effectiveness of conservation measures.
Evaluating Groundwater Use Claims
– Groups present their findings
– Class votes on claim validity
– Discuss sustainable groundwater use
– What actions can maintain our groundwater?
– Strategies for conservation
– Ideas: Reduce water waste, prevent pollution, replenish aquifers
|
This slide sets the stage for an interactive class discussion on the use of groundwater resources. Each group will present their research on various claims about groundwater use, allowing the class to critically evaluate the information presented. After each presentation, the class will vote on whether they believe each claim is valid, fostering a deeper understanding of how to assess environmental information. The discussion will then shift to sustainable practices, with a focus on how students can contribute to groundwater conservation. Encourage students to think about daily water usage, the impact of pollution on aquifers, and the importance of recharging groundwater sources. Provide examples of conservation methods, such as rainwater harvesting or using drought-resistant plants in landscaping.
Conclusion: Groundwater Conservation
– Recap groundwater significance
– Groundwater is crucial for drinking, agriculture, and ecosystems.
– Reflect on protecting groundwater
– Consider daily habits that impact groundwater and how to mitigate negative effects.
– Homework: Conservation paragraph
– Write about personal actions to conserve groundwater at home or in the community.
|
As we conclude our lesson on groundwater, it’s important to emphasize its vital role in our lives and the environment. Groundwater is a key source of fresh water for many purposes, including drinking, farming, and sustaining natural habitats. Encourage students to think critically about how their actions can affect groundwater levels and purity. For homework, they should write a paragraph reflecting on what they’ve learned and describe specific ways they can contribute to groundwater conservation in their daily lives. This exercise will help them apply their knowledge and foster a sense of responsibility towards environmental stewardship.