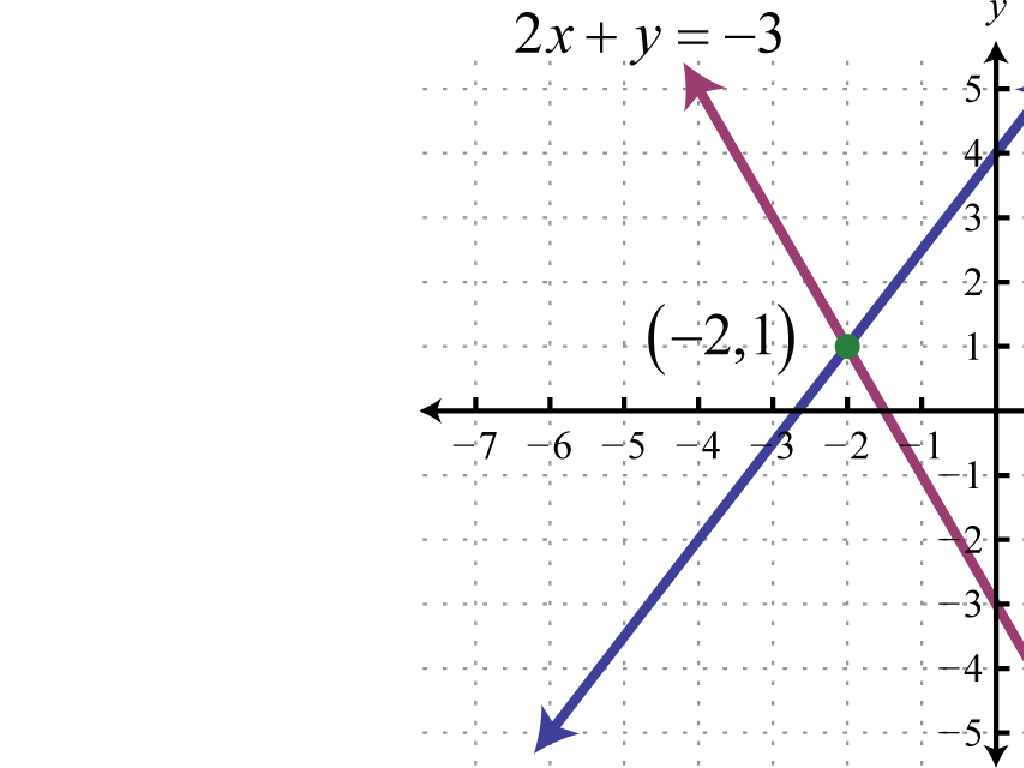
Spectroscopy
Subject: Science
Grade: High school
Topic: Organic Chemistry
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Introduction to Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry
– Spectroscopy: A powerful tool
– It’s the study of how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation.
– Identifying substances with Spectroscopy
– Used to determine the composition of organic compounds.
– Spectroscopy’s role in Organic Chemistry
– Essential for understanding molecular structure and bonding.
– Outline of today’s Spectroscopy lesson
|
Spectroscopy is a fundamental technique in organic chemistry that allows scientists to analyze the structure of molecules by observing their interaction with various forms of electromagnetic radiation. It’s crucial for identifying unknown substances and understanding their properties. Today’s lesson will cover the basics of spectroscopy, its significance in organic chemistry, and how it’s applied to identify different substances. We’ll explore different types of spectroscopic methods and their applications in real-world scenarios. Encourage students to think of spectroscopy like a detective’s tool for molecules, providing clues about their identity and structure.
Exploring Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry
– Spectroscopy defined
– A technique to analyze matter through its light absorption and emission
– Light’s interaction with matter
– When light interacts with molecules, it can be absorbed or emitted, revealing information about the substance
– Types of Spectroscopy
– Includes methods like Absorption, Emission, NMR, and Infrared
– Spectroscopy applications
|
Spectroscopy is a scientific method used to analyze the properties of organic compounds by observing the interaction of light with matter. It’s a fundamental tool in organic chemistry that allows scientists to identify substances and understand their structure and behavior. When light interacts with molecules, it can be absorbed or emitted at different wavelengths, which is characteristic of the substance. Different types of spectroscopy, such as Absorption, Emission, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), and Infrared (IR), provide various insights into the molecular world. This slide will introduce students to the concept of spectroscopy and its significance in the field of organic chemistry. Encourage students to think about how light behaves differently with different substances and the practical applications of this knowledge in real-world scenarios.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Spectroscopy
– Explore spectrum regions
– Ranges from radio waves to gamma rays
– Energy, wavelength, frequency
– Energy inversely related to wavelength
– Spectroscopy’s relation to spectrum
– Spectroscopy uses light absorption to analyze substances
– Practical applications in science
|
This slide aims to introduce students to the concept of the Electromagnetic Spectrum and its relevance to Spectroscopy in the context of Organic Chemistry. Begin by exploring the different regions of the spectrum, from the longest wavelengths like radio waves to the shortest like gamma rays. Explain the relationship between energy, wavelength, and frequency, emphasizing that energy is inversely proportional to wavelength. Highlight how Spectroscopy is related to the Electromagnetic Spectrum, as it is a technique that measures the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. Discuss practical applications, such as identifying chemical compounds and analyzing molecular structures. Encourage students to think about how this technology is used in real-world scenarios, like medical imaging and forensic analysis.
Applications of Spectroscopy in Various Fields
– Spectroscopy in pharmaceuticals
– Essential for drug composition analysis and quality control.
– Environmental monitoring uses
– Tracks pollutants, analyzes atmospheric conditions.
– Forensic analysis applications
– Helps in identifying substances at crime scenes.
– Spectroscopic techniques’ importance
|
This slide aims to highlight the practical applications of spectroscopy beyond the classroom. In the pharmaceutical industry, spectroscopy is crucial for determining the composition of drugs and ensuring their quality. Environmental monitoring relies on spectroscopic techniques to track pollutants and analyze atmospheric samples, which is vital for ecological research and public health. Forensic analysis uses spectroscopy to identify unknown substances at crime scenes, which can be pivotal in solving cases. Understanding these applications can help students appreciate the real-world significance of spectroscopy in various sectors.
Types of Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry
– Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
– Explores the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei
– Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
– Measures molecular vibrations for functional group identification
– Mass Spectrometry (MS)
– Determines the molecular weight and structure of compounds
– Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
– Analyzes the absorption of light to quantify and identify molecules
|
This slide introduces students to the various types of spectroscopy used in organic chemistry. NMR spectroscopy utilizes the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine the structure of organic compounds. IR spectroscopy is used to identify functional groups within molecules based on their vibrational transitions. Mass spectrometry helps in finding the molecular weight and structure by analyzing the mass of the molecule’s ionized fragments. UV-Vis spectroscopy measures the absorption of ultraviolet or visible light by molecules, which can be used to determine the concentration of the substance. Each method provides unique information that can be used to deduce the structure and characteristics of organic compounds.
In-Depth Look: Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
– IR Spectroscopy and functional groups
– IR Spectroscopy identifies molecular vibrations that are unique to functional groups.
– Interpreting IR spectrum peaks
– Peaks correspond to specific bond vibrations; their position and intensity reveal molecular structure.
– Examples of IR spectra
– Compare spectra of known substances with unknowns to determine structure.
– Practical applications of IR
– Used in quality control, environmental monitoring, and pharmaceuticals.
|
This slide delves into the specifics of Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy, a powerful tool in organic chemistry for identifying functional groups within molecules. Students should understand that IR Spectroscopy works by detecting vibrations in molecular bonds, which occur at different frequencies depending on the bond type. The resulting spectrum displays peaks that correspond to these frequencies. By reading an IR spectrum, chemists can deduce the presence of certain functional groups in a molecule. Provide examples of IR spectra to illustrate how different molecules produce distinct spectra. Discuss how IR Spectroscopy is applied in various industries, such as ensuring the purity of compounds in pharmaceuticals or detecting pollutants in the environment. Encourage students to think about how this technique is a vital part of modern chemical analysis.
In-Depth Look: NMR Spectroscopy
– Principles of NMR: Spin states
– Nuclei with odd mass or atomic numbers have spin states, affected by magnetic fields.
– Role of magnetic fields in NMR
– Understanding chemical shifts
– Chemical shifts occur due to electron shielding; they indicate the environment of nuclei.
– Interpreting NMR spectra
– Example: Ethanol’s NMR shows 3 distinct peaks corresponding to its 3 different types of hydrogen atoms.
|
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy is a powerful analytical tool in organic chemistry that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei. Begin with explaining the concept of nuclear spin states and how they are influenced by external magnetic fields. No need to elaborate on magnetic fields as the concept is straightforward. Then, discuss chemical shifts, which are small changes in the resonance frequency of a nucleus caused by the surrounding electron cloud. Provide an example, such as ethanol, to illustrate how NMR spectra can be interpreted to deduce the structure of organic compounds. Encourage students to practice interpreting spectra with various examples.
Class Activity: Spectroscopy Analysis
– Group activity: Analyze spectra
– Identify compounds with IR, NMR
– Use IR data to determine functional groups, NMR to identify molecule structure
– Present findings to the class
– Each group will explain their analysis process and conclusions
|
This class activity is designed to engage students in hands-on learning with spectroscopy. Divide the class into small groups and provide each with different spectra to analyze. Students will use infrared (IR) spectroscopy to identify functional groups within a molecule and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy to understand the molecule’s structure. After analysis, groups will present their findings, explaining how they used the data to identify the compounds. This activity will help students to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations, enhancing their understanding of spectroscopy in organic chemistry. Possible activities include identifying unknown samples, comparing spectra of known compounds, or even predicting the structure of molecules based on their spectra.
Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry: Conclusion & Q&A
– Recap: Spectroscopy’s role
– Its importance in Organic Chem
– Essential for identifying compounds
– Encourage questions
– Homework: Spectroscopy application
– Find how Spectroscopy is used in industries or research
|
As we conclude our lesson on Spectroscopy, it’s crucial to emphasize its significance in identifying and analyzing organic compounds. This technique is indispensable for chemists in both academic and industrial settings. Encourage students to ask any questions they may have to clarify their understanding. For homework, students should research how Spectroscopy is applied in the real world, such as in pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, or forensics, to reinforce the practical relevance of what they’ve learned. This task will also help them appreciate the value of Spectroscopy beyond the classroom.