Area Of Compound Figures With Triangles
Subject: Math
Grade: Sixth grade
Topic: Perimeter And Area
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Exploring Perimeter and Area
– Understanding space around us
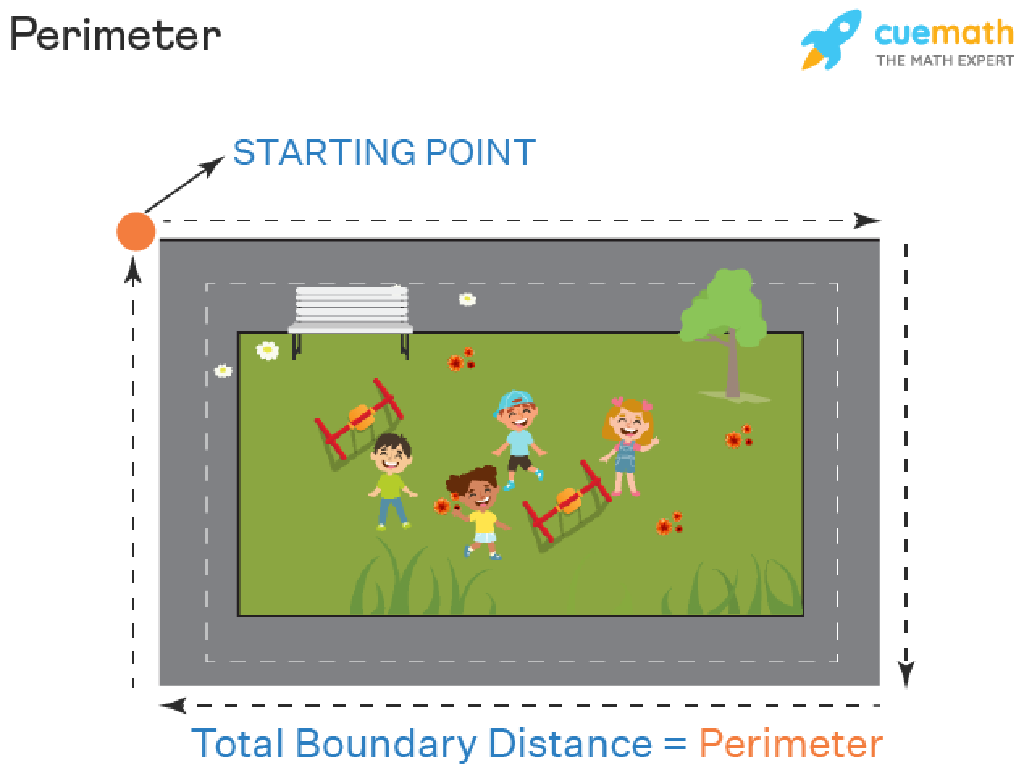
– Recap on perimeter
– Perimeter is the total distance around a shape
– Introduction to area
– Area measures the space inside a 2D shape
– Area of compound figures
– Combining areas of simple shapes to find the area of a complex figure
|
This slide introduces the concepts of perimeter and area, which are fundamental in understanding the space around us and within shapes. Begin by discussing how we interact with space in our daily lives. Recap the definition of perimeter by reminding students that it’s the total length around a shape, which they can find by adding all the sides. Introduce the concept of area as a measure of the space inside a shape, calculated in square units. Emphasize that understanding the area is crucial when dealing with compound figures, which can be broken down into simpler shapes like triangles, rectangles, and circles. Provide examples of compound figures and demonstrate how to calculate their area by adding the areas of the individual shapes. Encourage students to think of real-life examples where they might need to calculate area and perimeter.
Understanding Area: Compound Figures
– Area: space within a shape
– Measuring area in square units
– Like square inches (in²), square meters (m²)
– Rectangle area: length times width
– If a rectangle is 5m by 3m, its area is 15m²
– Breaking down compound shapes
– Divide compound shapes into rectangles and triangles
|
This slide introduces the concept of area, focusing on understanding the space inside two-dimensional shapes. Area is measured in square units, which could be inches, feet, meters, etc., depending on the context. For rectangles, the area is found by multiplying the length by the width. When dealing with compound figures that include triangles, students should learn to break down the figure into simpler shapes (rectangles and triangles) and calculate the area of each before summing them up to find the total area. This foundational knowledge will be crucial as they move on to more complex figures. Encourage students to practice with different compound shapes as homework.
Exploring Triangles and Their Areas
– Classify triangles by sides and angles
– Types include equilateral, isosceles, scalene, acute, obtuse, and right triangles.
– Area formula for triangles
– To find area, use formula: (base x height) / 2.
– Practice: Area of a right triangle
– Example: Right triangle with base 6 cm, height 8 cm. Area = (6 x 8) / 2 = 24 cm².
|
Begin by discussing the different types of triangles, focusing on the characteristics that distinguish them by sides (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and angles (acute, obtuse, right). Emphasize the importance of understanding these types before moving on to calculating areas. Introduce the formula for the area of a triangle and explain each component (base and height). For the practice problem, provide a right triangle with specific measurements and guide students through the process of applying the formula to find the area. Encourage students to solve the problem on their own first, then discuss the solution as a class. This exercise will help solidify their understanding of the area calculation for triangles.
Understanding Compound Figures
– Define compound figures
– A shape made up of two or more simple shapes
– Break down into simpler shapes
– Divide the figure into rectangles, triangles, etc.
– Example: Rectangle and triangle combo
– Consider a shape with a base rectangle and a triangle on top
– Calculate area step-by-step
– Add the areas of the rectangle and triangle together
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of compound figures, which are shapes that consist of two or more simple shapes combined. Start by defining compound figures and explaining that they can be broken down into simpler shapes like rectangles and triangles. Use an example of a compound figure composed of a rectangle and a triangle to demonstrate how to find the area. Walk through the process of calculating the area of each simple shape separately and then adding those areas together to find the total area of the compound figure. Encourage students to practice with different compound shapes and to always look for ways to simplify complex figures into shapes they are familiar with.
Calculating Area of Compound Figures
– Identify simple shapes in the figure
– Look for triangles, rectangles, etc.
– Calculate area of each shape
– Use correct formula for each shape
– Add or subtract areas for total
– Add areas if shapes are together, subtract if one is inside another
– Practice with different figures
|
This slide is aimed at teaching students how to approach finding the area of compound figures, which are shapes made up of two or more simple shapes. Start by guiding students to recognize and label all the basic shapes within a compound figure. Then, move on to calculating the area of each individual shape using the appropriate formula (e.g., for a rectangle, area = length × width; for a triangle, area = 1/2 × base × height). After finding the areas of all the simple shapes, students will either add or subtract these areas to find the total area of the compound figure, depending on whether the shapes are combined or one is within another. Encourage students to practice with various examples to solidify their understanding. Provide additional problems that include different combinations of shapes and ask students to explain their reasoning.
Let’s Practice Together: Area of Compound Figures
– Class activity: Calculate compound figure area
– Use area formulas for rectangles and triangles
– Work in pairs for problem-solving
– Collaboration can lead to better understanding
– Share solutions and methods with class
– Discuss different approaches and learn from peers
|
This slide introduces a collaborative class activity focused on calculating the area of compound figures that include triangles. Students are to work in pairs, which encourages teamwork and allows them to discuss their problem-solving strategies. This activity will help them apply their knowledge of area formulas for both rectangles and triangles in a practical setting. After completing the activity, each pair will share their solution and the method they used with the class, providing an opportunity for peer learning. As a teacher, facilitate the activity by providing guidance and ensuring each pair understands the task. Possible activities could include calculating the area of a park with different playground equipment shapes or a sports field with various marked areas.
Real-World Application of Area
– Importance of knowing area
Area measures the size of a surface. It’s used in building, farming, and more.
– Area in garden planning
When planning a garden, knowing the area helps decide how much space plants need.
– Discussing area applications
Think about where else area is important – in sports fields, home design, etc.
– Encouraging practical thinking
|
Understanding the concept of area is crucial for various real-world applications. For instance, when planning a garden, one must calculate the area to determine how many plants can fit or how much material is needed for a space. Encourage students to think about other areas in life where measuring area is essential, such as in constructing homes, creating sports fields, or even hanging wallpaper. This discussion will help them appreciate the practicality of math in everyday life. Provide examples and ask students to come up with their own, fostering an interactive learning environment.
Class Activity: Create Your Compound Figure
– Draw a unique compound figure
– Calculate the total area
– Break down the figure into simple shapes, find each area, then sum up
– Present and explain your work
– Share your figure and calculation steps with the class
– Reflect on the activity
– Think about what was challenging or interesting
|
This activity is designed to reinforce students’ understanding of calculating the area of compound figures that include triangles. Students will apply their knowledge of area calculation for simple shapes to more complex figures. Provide them with graph paper to assist in accurate drawing and calculation. Encourage creativity in their designs. As they present, they should explain how they divided their figure into simpler shapes, calculated each area, and then combined these to find the total area. After presentations, lead a discussion on the different strategies used and what they learned from the exercise. Possible variations for different students could include using different sets of shapes, adding constraints like a maximum number of shapes, or incorporating real-life objects into their figures.
Wrapping Up: Area of Compound Figures
– Review of compound figures area
– Homework: textbook compound figures
– Find and calculate the area of various compound figures assigned.
– Study for upcoming area quiz
– Review today’s lesson to prepare for the quiz.
– Practice makes perfect!
– The more you practice, the better you’ll understand.
|
As we conclude today’s lesson on the area of compound figures with triangles, it’s important for students to reinforce what they’ve learned by completing homework from their textbook. Assign specific problems that involve calculating the area of compound figures. Remind students to use the strategies discussed in class, such as breaking down figures into simpler shapes and applying the appropriate formulas. Encourage them to study the concepts in preparation for a quiz during the next class. Emphasize the importance of practice in mastering the topic and provide additional resources or office hours for students who may need extra help.