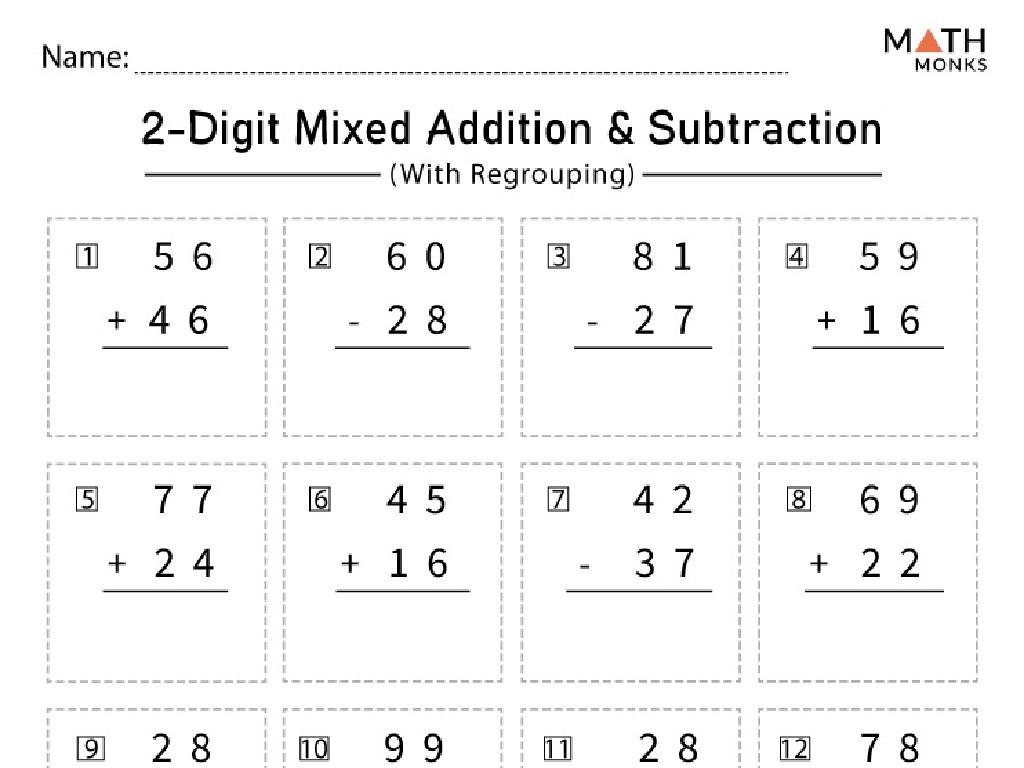
Addition And Subtraction Terms
Subject: Math
Grade: Second grade
Topic: Properties
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Welcome to Math Properties!
– Learn Addition and Subtraction
– Understand math language
– Math has special words that help us solve problems.
– Become math detectives
– Use your detective skills to find hints in math problems.
– Discover clues to solve problems
– Clues like ‘altogether’ or ‘left’ help us know when to add or subtract.
|
Today’s lesson introduces the foundational concepts of addition and subtraction, which are critical building blocks in mathematics. We’ll explore the specific language used in math, such as ‘sum,’ ‘total,’ ‘difference,’ and ‘remaining,’ to help students understand how to approach and solve problems. By framing the lesson as a detective game, we can engage students in a fun and interactive way. Encourage them to look for keywords and phrases in problems that indicate which operation to use. This approach will help demystify math and make it more accessible and enjoyable for second graders.
Understanding Addition
– Addition: Combining groups
– Imagine putting two toy piles together
– Adding makes amounts larger
– If you have 3 apples and get 2 more, now you have 5
– Learn key addition terms
– Addend (numbers being added), Sum (the result), Plus (the sign +), Total (the sum)
– Practice with examples
|
This slide introduces the concept of addition to second-grade students. Start by explaining that addition is like combining groups of items, such as toys or candies, to make a bigger group. Use visual aids or physical objects to demonstrate this concept. Emphasize that when we add, the total number of items increases. Introduce the key terms ‘addend’ (the numbers we are adding), ‘sum’ (the final result), ‘plus’ (the addition symbol), and ‘total’ (another word for the sum). Provide simple examples and encourage students to use these terms when they describe addition problems. For instance, ‘3 plus 2 equals 5’ where 3 and 2 are addends, and 5 is the sum or total.
Let’s Practice Addition!
– Adding apples together
– Example: 2 apples + 3 apples = 5 apples
– Use fingers for help
– Count on fingers: 1, 2, and then 1, 2, 3
– Practice on the board
– We’ll add numbers as a class activity
– Solve 2 + 3
– What is 2 apples + 3 apples?
|
This slide is designed to engage second-grade students in a practical addition exercise. Start with a relatable example, such as adding apples, which they can visualize. Encourage students to use their fingers to count, as this tactile method supports their understanding of addition. Involve the class by solving addition problems on the board together, making it interactive. For the example given, demonstrate how to add 2 apples plus 3 apples by counting on fingers and then writing the equation on the board. Ask the students to participate by coming up to the board to try their own addition problems. This activity helps to reinforce the concept of addition and provides a foundation for learning more complex arithmetic.
Understanding Subtraction
– Subtraction means taking away
– If you have 5 apples and take away 2, you subtract 2 from 5.
– The amount becomes smaller
– Start with 5 apples, after taking 2 away, only 3 apples are left.
– Key terms: Minuend, Subtrahend, Difference
– Minuend is the number you start with, subtrahend is what you take away, and the difference is what’s left.
– Using ‘minus’ and ‘less’
– Words like ‘minus’ and ‘less’ signal subtraction: 5 apples minus 2 apples leaves 3 apples.
|
This slide introduces the basic concept of subtraction to second graders. Subtraction is explained as the process of taking away from a total amount, which results in a smaller number. The key terms are defined to familiarize students with the vocabulary of subtraction: ‘minuend’ (the starting number), ‘subtrahend’ (the number you take away), and ‘difference’ (the result). Illustrate the concept with simple, relatable examples, such as subtracting items like apples. Emphasize the action words ‘minus’ and ‘less’ as indicators of subtraction in problems. Encourage students to use objects or their fingers to practice subtracting and to understand the terms in a tangible way.
Let’s Practice Subtraction!
– Example: 5 stars – 2 stars = ?
– What’s left when we take 2 stars from 5?
– Use objects or drawings to subtract
– Visual aids make subtraction easier to grasp
– Solve subtraction problems together
– We’ll work as a team to find the answers
– Understand subtraction concept
|
This slide is designed to engage second-grade students in a hands-on subtraction activity. Start with a simple example using stars to demonstrate subtraction. Encourage students to use physical objects like counters or to draw pictures to visualize the subtraction process. Work through several problems as a class, guiding students to understand that subtraction means taking away. Ask students to explain their thought process and how they arrived at their answers. This will help solidify their understanding of subtraction as they relate it to tangible items or visual representations.
Magic Stones: Learning Addition & Subtraction
– Starting with 4 magic stones
– Finding 3 more stones
Now you have 4 + 3 stones. How many is that?
– Giving 2 stones to a wizard
You had 7, but give 2 to the wizard. Now how many?
– Stories make math fun and easy
|
This slide uses a magical story to help second graders understand the concepts of addition and subtraction. Start by engaging their imagination with the idea of having magic stones. Then, through the story, introduce the addition of more stones and the subtraction when giving some away to a wizard. This narrative approach makes the math concepts more relatable and easier to grasp for young learners. Encourage the students to visualize the stones in their hands as they perform the calculations, and to share their answers with the class. This interactive storytelling method reinforces their understanding of basic arithmetic operations within a fun and memorable context.
Math Properties: Addition and Subtraction
– Addition order can change
– Commutative Property of Addition
– 3 + 4 is the same as 4 + 3
– Subtraction order matters
– Changing order changes the result
– 5 – 3 is not the same as 3 – 5
|
This slide introduces the Commutative Property of Addition, which states that numbers can be added in any order without changing the result. Use simple examples like 3 + 4 and 4 + 3 to illustrate this property. Contrast this with subtraction, where the order of numbers is crucial; for example, 5 – 3 does not equal 3 – 5. Emphasize that while addition is flexible, subtraction is not. Encourage students to practice with different numbers to see the property in action. This will help them understand the fundamental differences between addition and subtraction.
Class Activity: Math Scavenger Hunt
– Find classroom objects to add or subtract
– Pair up to write math stories
– Use objects found to create fun stories involving adding or taking away
– Share your stories with the class
– Take turns telling your math stories to the class
– Discuss the addition and subtraction
– Talk about how you added or subtracted in your story
|
This interactive activity is designed to help second graders understand addition and subtraction through a hands-on experience. Students will work in pairs to search for items in the classroom that they can use in their own math stories, promoting teamwork and creativity. After crafting their stories, each pair will present to the class, explaining how they used addition or subtraction. Encourage students to listen to others’ stories and understand different approaches to problem-solving. Possible activities: 1) Counting pencils and erasers to find a total, 2) Adding books from different shelves, 3) Subtracting crayons from a box, 4) Combining groups of blocks, 5) Taking away pieces from a puzzle.