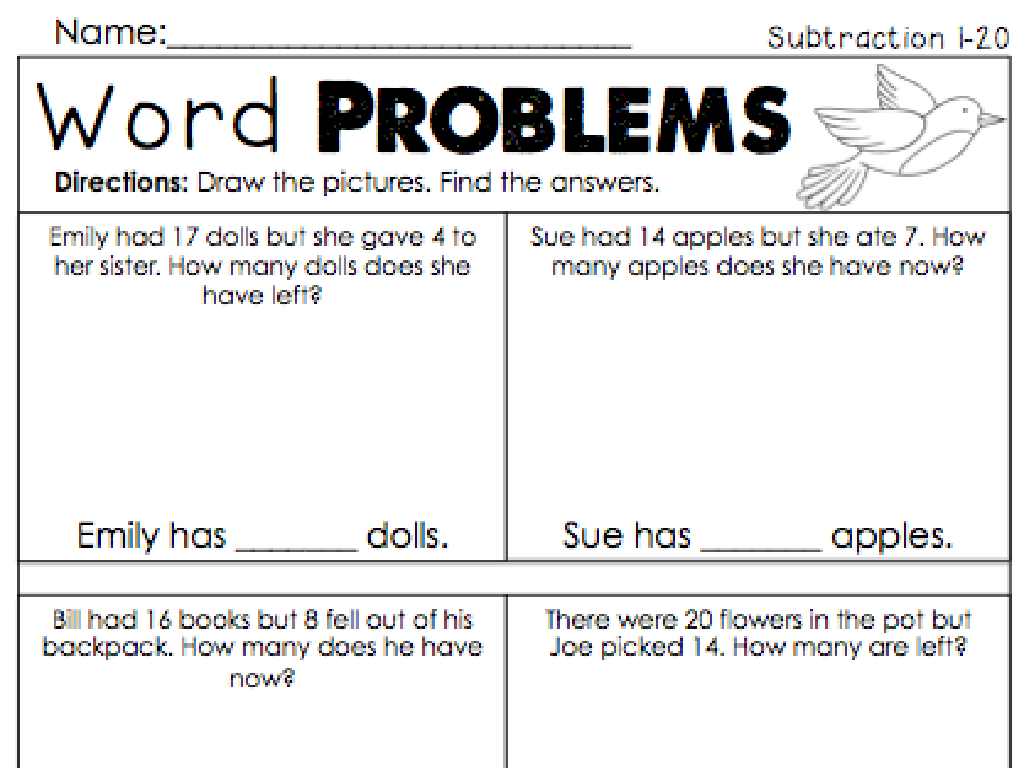
Add And Subtract Rational Numbers: Word Problems
Subject: Math
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: Rational Numbers
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Adding and Subtracting Rational Numbers
– Define rational numbers
– Numbers that can be expressed as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers and b is not zero.
– Real-world rational number examples
– Money, measurements, and time can all be examples of rational numbers in daily life.
– Adding rational numbers
– When adding, find a common denominator and then add the numerators.
– Subtracting rational numbers
– To subtract, find a common denominator, then subtract the numerators.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of rational numbers and their application in real-life scenarios. Begin by defining rational numbers and ensuring students understand the fraction representation. Provide relatable examples such as money (dollars and cents), measurements (meters and centimeters), and time (hours and minutes) to illustrate rational numbers in everyday life. Then, guide students through the process of adding and subtracting rational numbers, emphasizing the importance of finding a common denominator for both operations. Encourage students to practice with word problems that involve adding and subtracting rational numbers to solidify their understanding.
Exploring Rational Numbers
– Define rational numbers
– Numbers expressed as a fraction of two integers, e.g., 1/2, 3/4, 7, -6
– Examples vs. non-examples
– Examples: 1/2, 0.75; Non-examples: 2, À
– Place numbers on a number line
– Visualize ordering of fractions, decimals, and whole numbers
– Understanding through word problems
|
Begin with a clear definition of rational numbers, emphasizing that they can be written as a fraction where both numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero. Provide clear examples of rational numbers, including both positive and negative fractions and decimals, and contrast these with non-examples like irrational numbers. Demonstrate how to place these numbers on a number line to give students a visual understanding of their order and relative value. Introduce word problems to apply this knowledge, ensuring students can identify and compute with rational numbers in practical scenarios.
Adding Rational Numbers
– Rules for adding rational numbers
– Keep the same denominator, add the numerators
– Visualize addition on number lines
– Use points to represent numbers and show movement
– Example: Adding like denominators
– 1/4 + 1/4 = 2/4 or simplified to 1/2
– Practice with real-world problems
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of adding rational numbers, focusing on the rules and visualization techniques. Start by explaining that when adding fractions with like denominators, we simply add the numerators while keeping the denominator the same. Demonstrate this with an example on the slide. Then, show how to use a number line to represent and add rational numbers, which helps in understanding the concept of magnitude and direction in addition. Provide students with additional real-world word problems to apply these concepts, ensuring they get practical experience. Encourage students to simplify their answers whenever possible, reinforcing the concept of equivalent fractions.
Subtracting Rational Numbers
– Rules for subtraction
– Change to addition and use the opposite of the number being subtracted.
– Visualize with number lines
– A number line can show the distance between numbers and direction of subtraction.
– Example: Unlike denominators
– Subtract 3/4 – 1/6 by finding a common denominator, then subtract numerators.
– Practice problem set
|
When teaching subtraction of rational numbers, start by explaining the rules, such as converting a subtraction problem into an addition problem by adding the opposite. Use a number line to help students visualize the process as it provides a clear representation of the distance and direction when subtracting values. Work through an example with fractions that have unlike denominators, showing how to find a common denominator before subtracting. Provide a set of practice problems for students to apply these concepts, ensuring a variety of rational numbers, including fractions, decimals, and integers, to solidify their understanding.
Word Problems: Adding Rational Numbers
– Comprehend the problem scenario
– Read carefully to grasp the situation.
– Highlight crucial numerical data
– Look for and underline all important numbers and their relationships.
– Execute step-by-step solution
– Follow mathematical operations in order, showing all work.
– Verify results with the context
– Check if the answer makes sense within the problem’s story.
|
This slide is aimed at guiding students through the process of solving addition word problems involving rational numbers. Start by ensuring students understand the context of the problem; they should read the problem multiple times if necessary. Teach them to identify and underline key information such as the numbers involved and what is being asked. Then, demonstrate how to approach the problem in a structured manner, solving it step by step and writing down each step to avoid confusion. Finally, emphasize the importance of verifying their answers by checking if it logically fits into the context of the problem. Encourage students to practice with various word problems to build their confidence and proficiency.
Subtracting Rational Numbers: Word Problems
– Comprehend the problem scenario
– Read carefully to grasp the context
– Highlight crucial information
– Look for numbers, operations, and the question
– Solve the problem methodically
– Use subtraction of rational numbers step by step
– Review and verify your solution
– Check if the answer makes sense in the problem
|
This slide is aimed at guiding students through the process of solving word problems involving the subtraction of rational numbers. Start by ensuring students understand the context of the problem; what is the scenario, and what is being asked? Teach them to identify and underline key pieces of information, such as the numbers involved and the operation required. Walk them through a step-by-step approach to solve the problem, emphasizing the correct application of subtraction for rational numbers. Finally, encourage them to review their solution to ensure it logically fits the context of the problem. Provide an example problem and solve it together as a class, then assign similar problems for individual practice.
Practice Problems: Adding & Subtracting Rational Numbers
– Solve word problems together
– Apply learned concepts
– Use strategies from our lessons to tackle new problems
– Share and discuss solutions
– Explain your reasoning and listen to others’ approaches
– Explore various methods
– There’s often more than one way to solve a problem, let’s find them!
|
This slide is designed to engage students in active problem-solving and to reinforce their understanding of adding and subtracting rational numbers through practical application. Start by solving a few problems as a class, guiding students through the process and encouraging them to apply the concepts they’ve learned. Then, have students share their solutions and discuss the different methods used to arrive at the answers. Emphasize the importance of understanding the process over just getting the right answer. Encourage students to explain their reasoning and to be open to learning from different approaches. This collaborative activity not only solidifies their learning but also fosters a supportive learning environment.
Class Activity: Rational Numbers Relay
– Form teams for the relay
– Each member solves a step
– Pass your solution to the next person
– First team with correct answer wins!
|
This activity is designed to encourage teamwork and understanding of rational numbers through a relay race format. Divide the class into small groups, and provide each team with a multi-step rational number problem. Each member is responsible for solving one step of the problem before passing it on to the next team member. This will require students to communicate effectively and ensure each step is correct. The first team to arrive at the correct final answer wins the relay. Possible problems could include combining positive and negative fractions, adding and subtracting decimals, or mixed operations with rational numbers. Ensure that each problem is appropriately challenging for the grade level and that all necessary materials are prepared in advance.