Multiply And Divide Rational Numbers
Subject: Math
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: Rational Numbers
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Welcome to Rational Numbers
– Define rational numbers
– Numbers expressed as a fraction of two integers
– Explore examples of rational numbers
– For instance, 1/2, -3/4, and 5 are all rational numbers
– Discuss the importance in math
– They are foundational for algebra and beyond
– Learn multiplication and division
– Applying operations to fractions and whole numbers
|
This slide introduces the concept of rational numbers, which are any numbers that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers. The numerator and the denominator in a rational number are both integers, with the denominator not equal to zero. Provide examples such as 1/2, -3/4, and even whole numbers like 5 (which can be written as 5/1). Emphasize the importance of understanding rational numbers as they form the basis for more complex mathematical concepts in algebra, such as equations and functions. Demonstrate how to multiply and divide these numbers, ensuring to explain the rules for dealing with positive and negative signs. Encourage students to practice with examples and prepare them for applying these operations in various mathematical contexts.
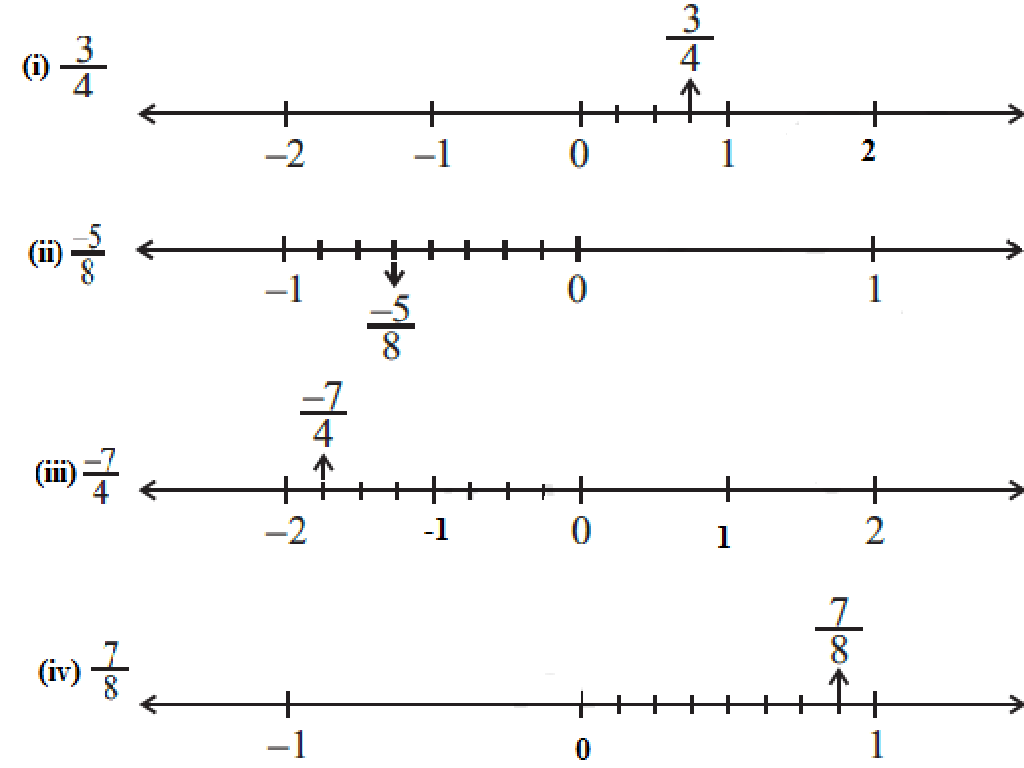
Understanding Rational Numbers
– Definition of rational numbers
– A number that can be expressed as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers and b is not zero.
– Rational numbers as ratios
– Think of it as a ratio, e.g., 1/2, 3/4, or 5/1, representing parts of a whole.
– Identifying rational numbers
– Can you spot the rational number: 1/3, À, 0.75, 2?
– Rational numbers in daily life
– Money, measurements, and time often involve rational numbers like $0.50, 1.25 meters, or 0.5 hours.
|
This slide introduces the concept of rational numbers, which are numbers that can be written as a fraction where both the numerator and the denominator are integers, and the denominator is not zero. Emphasize the idea of ratios and provide relatable examples to help students understand the concept. Encourage students to identify rational numbers from a set of numbers, including integers, fractions, and decimals. Use everyday examples such as money, measurements, and time to show how rational numbers are used in real life. This will help students see the relevance of rational numbers to their daily activities and other subjects.
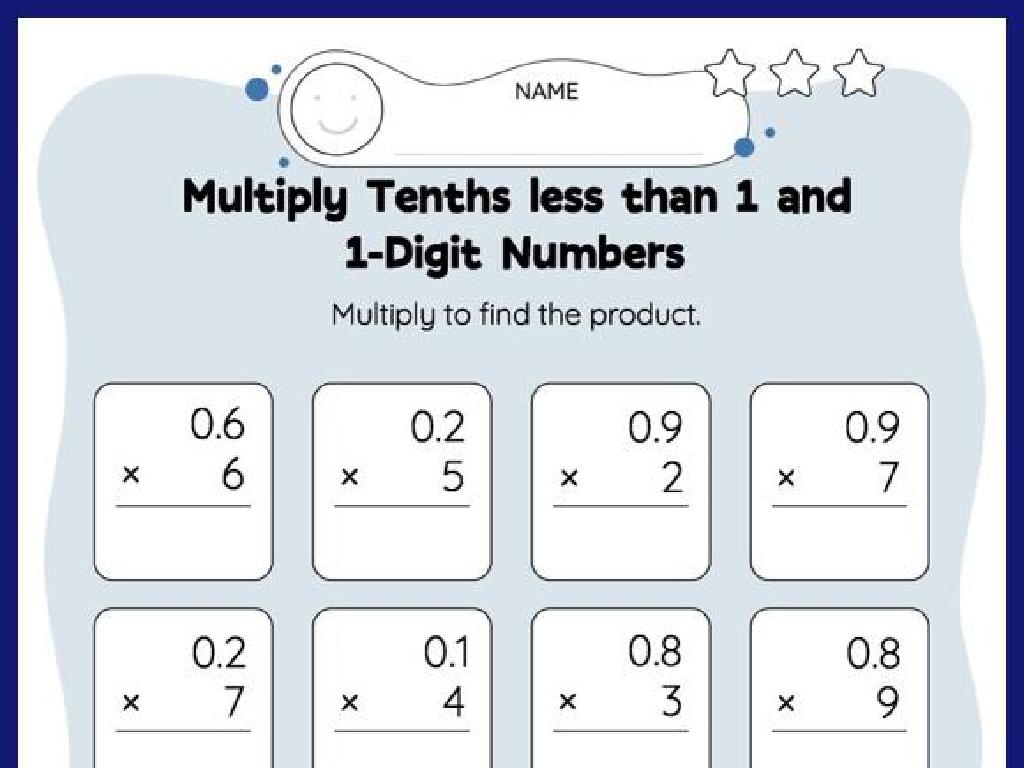
Multiplying Rational Numbers
– Rules for multiplying rationals
– Multiply numerators and denominators separately. Remember the sign rules.
– Multiplying fractions step-by-step
– To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators together and the denominators together.
– Multiplying decimals accurately
– Align decimal points and multiply as whole numbers, then place the decimal in the product.
– Ensuring a rational product
– The product of two rational numbers is always rational.
|
When teaching multiplication of rational numbers, start by reviewing the rules for multiplying positive and negative numbers. Emphasize that the product of two rational numbers, whether they are fractions or decimals, is also a rational number. Provide step-by-step guidance on multiplying fractions: multiply the top numbers (numerators) and then the bottom numbers (denominators), simplifying if possible. For decimals, teach students to multiply as if they were whole numbers and then place the decimal point in the correct position in the answer. Reinforce that the product must be in its simplest form to be considered rational. Include examples and practice problems to solidify understanding.
Multiplying Rational Numbers
– Multiply two fractions
– To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators and then the denominators. E.g., 3/4 * 2/3 = 6/12
– Fraction times a decimal
– Convert the decimal to a fraction, or vice versa, then multiply. E.g., 3/4 * 0.5 = 3/4 * 1/2 = 3/8
– Multiply two decimals
– Multiply as whole numbers, then place the decimal. E.g., 0.3 * 0.2 = 0.06
|
This slide focuses on demonstrating the multiplication of different types of rational numbers. Start with multiplying two fractions, ensuring students understand the process of multiplying numerators and denominators separately. Then, show how to multiply a fraction by a decimal, which may involve converting the decimal to a fraction for easier computation. Lastly, cover the multiplication of two decimals, emphasizing the correct placement of the decimal point in the final answer. Provide additional examples and encourage students to practice these methods with various numbers to build their confidence and proficiency.
Dividing Rational Numbers
– Rules for division with rational numbers
– Keep, Change, Flip: Keep the first number, change division to multiplication, flip the second number.
– Invert divisor to divide fractions
– Example: To divide 3/4 by 2/3, multiply 3/4 by 3/2.
– Steps for dividing decimals
– Align decimals, divide as whole numbers, place decimal in quotient.
|
When dividing rational numbers, students should remember the ‘Keep, Change, Flip’ rule, which simplifies the process of dividing fractions. By keeping the first fraction, changing the division sign to multiplication, and flipping the second fraction (taking its reciprocal), division becomes a more straightforward operation. For dividing decimals, ensure students understand how to align the decimal points and treat the numbers as whole numbers during division, placing the decimal in the quotient directly above its position in the dividend. Provide practice problems that reinforce these concepts and encourage students to explain the process in their own words.
Dividing Rational Numbers
– Divide two fractions (Example 1)
– To divide fractions, multiply by the reciprocal of the second fraction.
– Fraction divided by decimal (Example 2)
– Convert the decimal to a fraction, then multiply by the reciprocal.
– Divide two decimals (Example 3)
– Align the decimal points, then divide as with whole numbers.
|
This slide provides examples of dividing different forms of rational numbers. Start with dividing two fractions by multiplying the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second. For dividing a fraction by a decimal, first convert the decimal to a fraction and then proceed as with dividing two fractions. When dividing two decimals, ensure students understand how to align the decimal points and use long division as they would with whole numbers. Emphasize the importance of understanding these concepts as foundational skills for algebra. Provide additional practice problems for each example to reinforce learning.
Class Activity: Multiplying & Dividing Rational Numbers
– Practice multiplying rational numbers
– Practice dividing rational numbers
– Share your solutions with the class
– Compare answers and methods used
– Discuss different solving methods
– Understanding various approaches enhances problem-solving skills
|
This slide is designed for a class activity where students will engage in practicing the multiplication and division of rational numbers. Provide a set of problems for students to solve individually or in small groups. Encourage them to use different methods, such as cross-simplification before multiplying or finding the reciprocal before dividing. After completing the problems, students will share their answers and discuss the different methods they used to arrive at the solutions. This will help them see the variety of ways a problem can be approached and solved. As a teacher, facilitate the discussion to ensure that all students understand the correct procedures and can learn from each other’s strategies.
Class Activity: Rational Numbers Relay
– Form groups of four students
– Solve problems as a team
– Work together on rational number problems
– First team to finish wins
– Ensure all answers are correct to win
– Focus on multiplication and division
– Apply knowledge of multiplying and dividing rational numbers
|
This activity is designed to encourage teamwork and reinforce the students’ understanding of multiplying and dividing rational numbers. Divide the class into small groups and provide each group with a set of problems involving the multiplication and division of rational numbers. The first team to complete all problems correctly wins a small prize or recognition. Make sure to walk around and assist groups as needed. Possible variations of the activity could include a relay race where each student solves one problem before passing it on, or a ‘solve and check’ round where students must verify each other’s work before submitting their final answers.
Wrapping Up: Rational Numbers
– Review of multiplying/dividing rational numbers
– Mastery of rational numbers is crucial
– Understanding these concepts is key for future math topics
– Homework: Rational Numbers Worksheet
– Practice problems to solidify today’s lesson
– Be prepared to discuss solutions
– We’ll go over tricky problems in our next class
|
As we conclude today’s lesson on multiplying and dividing rational numbers, it’s important to emphasize the significance of mastering these concepts for future mathematical success. The homework assignment consists of a worksheet designed to reinforce the day’s learning and provide practice with a variety of problems. Encourage students to attempt all problems and remind them that we will review the most challenging ones in the next class. This will not only help them understand the material better but also allow them to share their approaches and learn from each other.