Identify The Complete Subject Of A Sentence
Subject: Language arts
Grade: Fourth grade
Topic: Sentences, Fragments, And Run-Ons
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Understanding Sentence Structures
– What makes a full sentence?
– A full sentence has a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought.
– Spotting sentence fragments
– Fragments are incomplete sentences missing a subject or verb.
– Avoiding run-on sentences
– Run-ons are sentences that need punctuation to break them into complete thoughts.
– Finding the complete subject
– The complete subject includes the main noun and all its modifiers.
|
Today’s lesson focuses on understanding the structure of sentences, identifying fragments, and correcting run-on sentences. The objective is to help students identify the complete subject within a sentence. A complete subject is more than just a noun; it includes all the words that describe the noun. Use examples to illustrate complete subjects, like ‘The quick brown fox’ instead of just ‘fox’. Have students practice by finding the complete subject in example sentences. Encourage them to explain why it’s complete, considering the modifiers that add detail to the main noun.
Exploring Sentences: The Subject
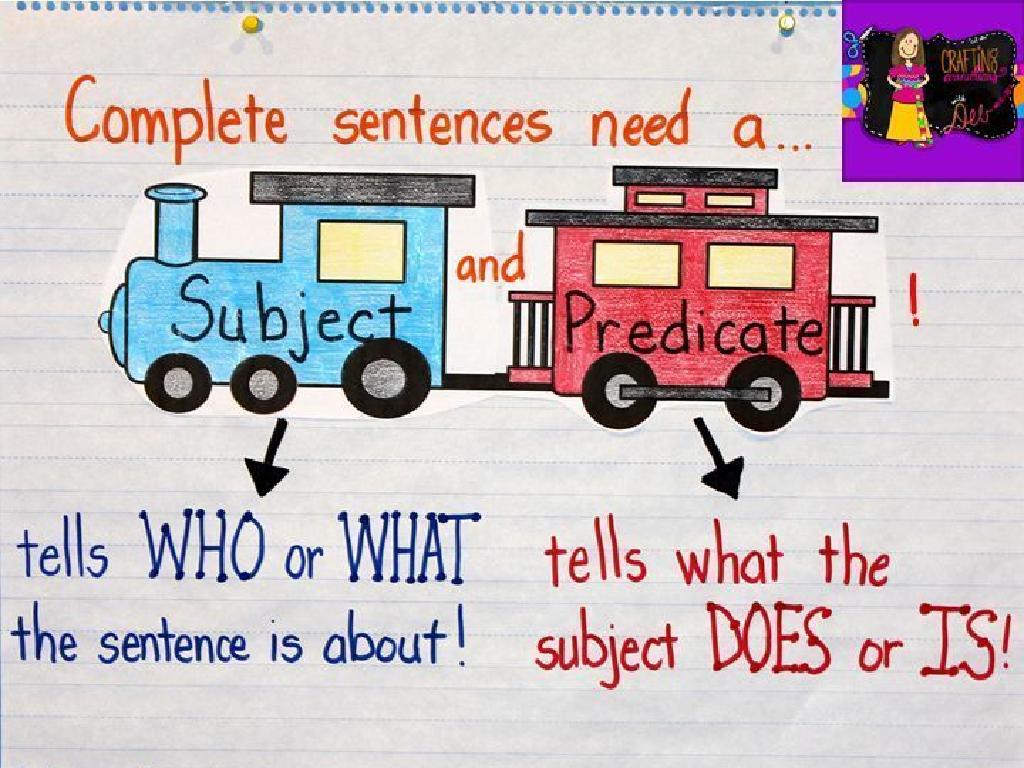
– A sentence: a complete thought
– Group of words that tell us what or who the sentence is about.
– Two main parts: subject and predicate
– Subject is who or what the sentence is about; predicate tells what the subject does or is.
– Today’s focus: the subject
– We’ll learn to find the who or what the sentence is about.
– Understanding the complete subject
– The complete subject includes all the words that tell us about the main part of the sentence.
|
Begin the lesson by defining a sentence and explaining that it is made up of a group of words that express a complete thought. Clarify that every sentence is composed of a subject and a predicate. The subject is what or who the sentence is about, while the predicate explains what the subject does or is. Today’s lesson will concentrate on identifying the complete subject in sentences. Emphasize that the complete subject includes all the words that describe the main ‘who’ or ‘what’ in the sentence, not just a single noun. Use examples to illustrate this and prepare exercises where students can practice identifying complete subjects.
Finding the Complete Subject in Sentences
– What is a subject?
– The subject is ‘who’ or ‘what’ the sentence is about.
– Subject can be one word
– Group of words: Complete Subject
– All words that tell us about the ‘who’ or ‘what’.
– Examples of complete subjects
– ‘The quick brown fox’ in ‘The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.’
|
This slide introduces the concept of the subject in a sentence, which is fundamental for understanding sentence structure. Start by explaining that the subject is the main focus of the sentence, usually a noun or pronoun. It can be simple, just one word, or complex, a group of words. The complete subject includes all the words that describe the subject, not just the noun. Use clear examples to illustrate the difference between a simple subject and a complete subject. Encourage students to practice by identifying the complete subject in various sentences. This will help them in writing more descriptive and detailed sentences.
Simple Subject vs. Complete Subject
– Simple subject: main word
– It’s the ‘who’ or ‘what’ of the sentence
– Complete subject: all telling words
– Includes descriptors and modifiers
– Examples of simple vs. complete
– ‘The quick brown fox’ vs. ‘fox’
– Practice identifying subjects
|
This slide introduces the concept of simple and complete subjects within a sentence. The simple subject is essentially the main noun or pronoun that the sentence is about, while the complete subject includes the simple subject and all the words that describe or modify it. Use examples to illustrate the difference, such as ‘The quick brown fox’ (complete subject) versus ‘fox’ (simple subject). Encourage students to practice by identifying the simple and complete subjects in sentences. Provide sentences and have them underline the simple subject once and the complete subject twice to visually distinguish between the two. This activity will help solidify their understanding of sentence structure.
Identifying Complete Subjects
– ‘The playful kitten’ example
– In ‘The playful kitten’ chased the string, ‘The playful kitten’ is who or what the sentence is about.
– ‘The playful kitten’ is the subject
– The complete subject tells us who performs the action in a sentence.
– Includes simple subject ‘kitten’
– The main noun in the subject is the ‘simple subject’.
– Descriptive words add detail
– Words like ‘playful’ give more information about the ‘kitten’.
|
This slide introduces the concept of the complete subject in a sentence. Use the example ‘The playful kitten’ chased the string to show that the complete subject is more than just the main noun; it includes all the words that describe the main noun, which is the simple subject. Explain that the complete subject can be thought of as the ‘who’ or ‘what’ of the sentence. Encourage students to identify the simple subject and the descriptive words that make up the complete subject in various sentences. Provide additional examples and practice sentences for students to work on individually or in groups.
Let’s Practice Identifying the Complete Subject!
– I’ll show sentences on the board
– Find the ‘who’ or ‘what’ in each
– Look for the main noun or pronoun
– Include all describing words
– Describing words give more info about the subject
– Are you ready to start?
|
This slide is designed to engage students in a class activity where they will practice identifying the complete subject in various sentences. The complete subject includes the ‘who’ or ‘what’ of the sentence along with all the words that describe it. Start by explaining that the complete subject is more than just a noun; it includes all the adjectives and articles that go with it. Then, show sentences on the board one by one and ask students to identify the complete subject. Encourage participation and provide guidance as needed. After each example, discuss as a class why the identified words make up the complete subject. This activity will help reinforce their understanding of sentence structure and prepare them for more complex grammar concepts.
Class Activity: Subject Hunt
– Let’s go on a subject hunt
– Find objects in our classroom
– Write sentences about them
– Write who or what the sentence is about
– Circle the complete subjects
– The complete subject includes all words that tell who or what the sentence is about
|
This interactive activity is designed to help students identify the complete subject in a sentence. Students will look for objects in the classroom and write sentences about them. For example, if a student chooses a clock, they might write, ‘The large round clock on the wall is ticking loudly.’ Here, ‘The large round clock on the wall’ is the complete subject. Encourage students to be descriptive in their subjects. After writing their sentences, students will circle the complete subjects. This exercise will reinforce their understanding of subjects in sentences and improve their ability to identify them in various contexts. Possible variations of the activity could include pairing up students, using classroom items in creative sentences, or even extending the hunt to outside the classroom if possible.
Review and Share: Complete Subjects
– Reviewing complete subjects
– Share your subject hunt sentences
– Read the sentences you created
– Identify classmates’ complete subjects
– Find the who or what the sentence is about
– Understanding subjects together
|
This slide is meant to consolidate the students’ understanding of complete subjects in sentences. Begin by reviewing the concept of a complete subject, which includes the ‘who’ or ‘what’ of the sentence along with all the words that describe it. Encourage students to share the sentences they crafted during the ‘subject hunt’ activity. As each student shares, ask the class to identify the complete subject in those sentences. This peer review process will help reinforce their learning and provide an opportunity for collaborative learning. Make sure to provide feedback and guide them through the process, ensuring that they understand how to identify the complete subject in any given sentence.
Homework Challenge: Complete Subjects in Stories
– Write your own short story
– Underline each complete subject
– The who or what the sentence is about
– Use a mix of subjects
– Try different people, animals, or things
– Get ready to share in class
|
This homework task is designed to help students practice identifying the complete subject in a sentence, which includes the main noun and all the words related to it. Encourage creativity in their writing and the use of a variety of subjects to make their stories interesting. Remind them that the complete subject is not just the main noun but also the words that describe or modify it. In the next class, select a few stories to share with everyone, discussing the complete subjects that were underlined. This will reinforce the concept and allow students to learn from each other’s work.