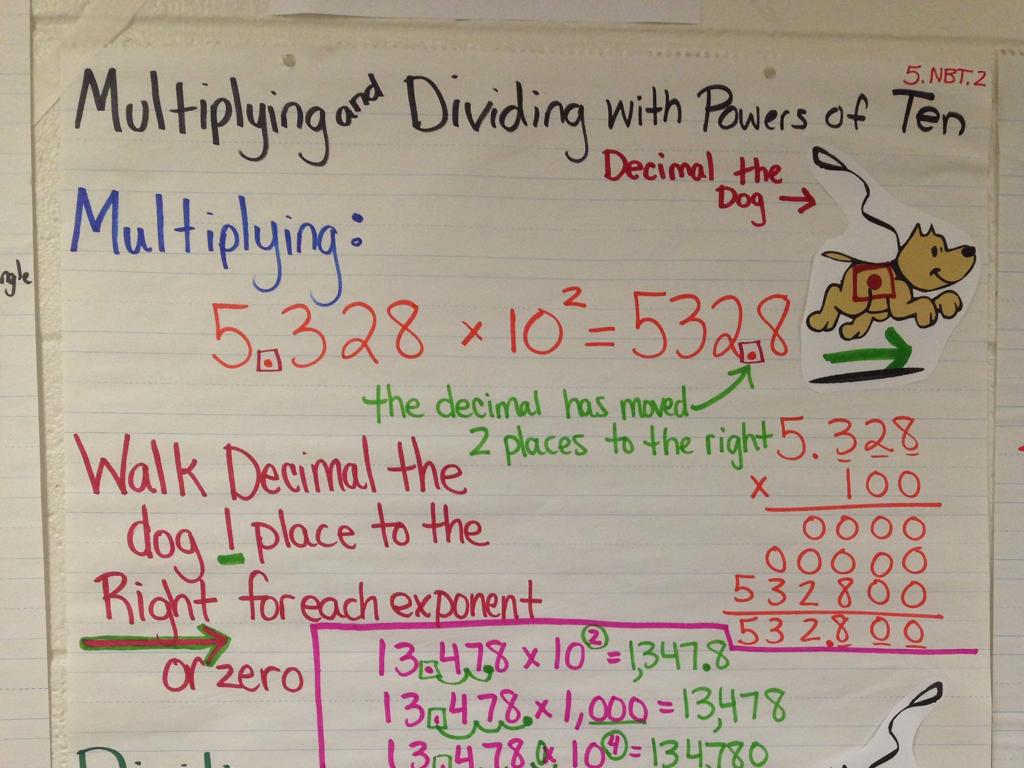The Revolutionary War: Struggle For Independence
Subject: Social studies
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: The American Revolution
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Introduction to the American Revolution
– Understanding the American Revolution
– A conflict that led to the creation of a new nation
– Significance of independence struggle
– The fight for liberty and self-governance was crucial
– Exploring the Revolutionary War
– Key battles and figures that shaped the war
– Objectives of today’s lesson
|
This slide introduces the American Revolution, setting the stage for the detailed study of the Revolutionary War. Begin by explaining the American Revolution as the colonial uprising against British rule, leading to the establishment of the United States. Emphasize the importance of the struggle for independence as a pivotal moment in history that set the precedent for democracy and freedom. Provide an overview of the Revolutionary War, including its key battles, strategies, and historical figures. The lesson’s objectives should focus on understanding the causes, the course, and the consequences of the war. Encourage students to think critically about the reasons behind the revolution and its lasting impact on the world.
Causes of the Revolutionary War
– ‘No taxation without representation’
– Colonists protested taxes imposed by a government in which they had no voice.
– Stamp Act’s role
– The Stamp Act of 1765 taxed paper goods, fueling discontent.
– Boston Tea Party’s impact
– The 1773 protest against tea taxes, symbolizing colonial resistance.
– Other key events pre-war
– Events like the Intolerable Acts and First Continental Congress were crucial.
|
This slide aims to outline the major causes leading up to the Revolutionary War, emphasizing the colonial resentment towards British taxation policies. The slogan ‘no taxation without representation’ encapsulated the colonists’ demand for a say in their governance. The Stamp Act was one of the first direct taxes on the colonies, leading to widespread protest. The Boston Tea Party became a defining moment of colonial opposition. Highlight other significant events that escalated tensions, such as the Intolerable Acts, which led to the convening of the First Continental Congress and ultimately the outbreak of war. Encourage students to consider how these events reflect the growing desire for independence and self-governance.
Key Figures in the Revolutionary War
– George Washington’s leadership
– First Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army
– Jefferson & Franklin’s contributions
– Authors of the Declaration, advocates for liberty
– France’s alliance and support
– Provided military aid, crucial to victory at Yorktown
– Impact of international involvement
|
This slide aims to introduce students to the influential leaders and nations that played a pivotal role in the American struggle for independence. George Washington’s leadership as the commander of the Continental Army was instrumental in the war effort. Thomas Jefferson and Benjamin Franklin were not only key figures in the drafting of the Declaration of Independence but also in garnering support for the revolutionary cause. The involvement of France, particularly their military support, was a turning point in the war, leading to the American victory at the Battle of Yorktown. Discuss the broader implications of international involvement in the war and how it shaped the outcome of the conflict. Encourage students to explore the diverse contributions of these figures and how their actions have had a lasting impact on the nation’s history.
Major Battles of the Revolutionary War
– Overview of Lexington & Concord
– First military engagements of the Revolutionary War, sparked the conflict.
– Significance of Saratoga
– Turning point of the war, gained French support for the Americans.
– Outcome of Siege of Yorktown
– Final battle, led to British surrender and end of the war.
|
This slide aims to highlight three pivotal battles in the American Revolutionary War that significantly influenced the struggle for independence. Begin with the Battle of Lexington and Concord, known as ‘the shot heard round the world,’ which initiated the war. Emphasize the strategic importance of the Battle of Saratoga as a turning point that secured French aid for the American cause. Conclude with the Siege of Yorktown, where British General Cornwallis’s surrender effectively ended the war and ensured American independence. Encourage students to understand the cause-and-effect relationship between these battles and the overall outcome of the war.
Life During the Revolutionary War
– Daily life of soldiers
– Soldiers faced hardships like scarce supplies and harsh conditions.
– Women’s roles in the war
– Women managed farms, businesses, and also served as nurses and spies.
– War’s impact on social groups
– Different groups experienced the war uniquely, with varying loyalties and challenges.
– Diversity of experiences
|
This slide aims to give students a glimpse into the personal side of the Revolutionary War. Discuss the daily struggles of soldiers, including lack of food, clothing, and shelter, and the constant threat of disease and battle. Highlight the significant contributions of women, who not only took on traditionally male roles at home but also directly supported the war effort. Address the varied impact on social groups, such as Loyalists, Patriots, Native Americans, and African Americans, and how the war affected their lives and communities. Encourage students to consider how the war might have looked from different perspectives and to think critically about the complexities of this historical period.
The Declaration of Independence
– Purpose of the Declaration
– To state the colonies’ intent to separate from British rule
– Analyze key document excerpts
– ‘We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal…’
– Global impact of the Declaration
– Inspired other nations towards democracy and independence
|
The Declaration of Independence was a pivotal document in American history, marking the formal separation of the Thirteen Colonies from Great Britain. Its purpose was to articulate the reasons for the colonies’ decision to seek independence and to declare that they were no longer under British rule. When analyzing key excerpts, focus on the ideals of liberty and equality, which have become foundational to American society. Discuss how the Declaration had a far-reaching global impact, serving as an inspiration for other countries and peoples fighting for their own freedom and democratic rights. Encourage students to consider how the principles outlined in the Declaration continue to influence the world today.
The Outcome and Legacy of the Revolutionary War
– Treaty of Paris 1783 terms
– Ended the war, recognized US independence, and set new borders
– War’s impact on the new nation
– Established a republic, influenced political ideas and society
– Long-term effects of the Revolution
– Sparked global democratic movements, changed social hierarchies
|
This slide aims to summarize the conclusion of the Revolutionary War and its lasting impact on the United States and the world. The Treaty of Paris 1783 formally ended the conflict, acknowledged American independence, and established borders for the new nation. The war’s outcome shaped the United States’ development as a republic and influenced its political ideologies, fostering a society that valued liberty and democratic principles. Additionally, the Revolution had far-reaching effects, inspiring democratic movements worldwide and altering traditional social structures. Encourage students to consider how the Revolution’s ideals continue to influence American society and government today.
Class Activity: Loyalists vs. Patriots Debate
– Divide into Loyalists and Patriots
– Research and prepare arguments
– Use historical facts to support your stance
– Engage in a mock debate
– Argue for or against independence
– Reflect on the perspectives
– Consider the values and concerns of both sides
|
This activity aims to deepen students’ understanding of the differing viewpoints during the Revolutionary War. By role-playing as Loyalists and Patriots, students will explore the complex motivations and arguments that existed on both sides of the conflict. Teachers should provide resources for each group to research their positions and prepare their arguments. During the debate, encourage respectful discourse and critical thinking. After the debate, lead a reflection session where students can discuss what they learned about the perspectives and how these debates shaped the path to war. Possible activities include writing a reflective essay, creating propaganda posters, or composing a speech from the viewpoint of their assigned role.