Laws And Courts
Subject: Social studies
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: The Constitution
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Introduction to Laws and Courts
– Purpose of laws in society
– Laws maintain order and protect rights
– Courts’ role in the Constitution
– Courts interpret and apply laws, ensuring they align with the Constitution
– Structure of the court system
– Includes Supreme, appellate, and district levels
– Today’s lesson overview
|
This slide introduces the fundamental concepts of laws and courts within the context of the U.S. Constitution. Begin by discussing the purpose of laws in society, emphasizing their role in maintaining order and protecting individual rights. Then, explain how courts function to uphold the Constitution by interpreting and applying laws. Outline the structure of the court system, including the Supreme Court, appellate courts, and district courts. Conclude with an overview of today’s lesson, which will delve deeper into each of these topics, providing students with a clear understanding of how laws and courts work together to govern society.
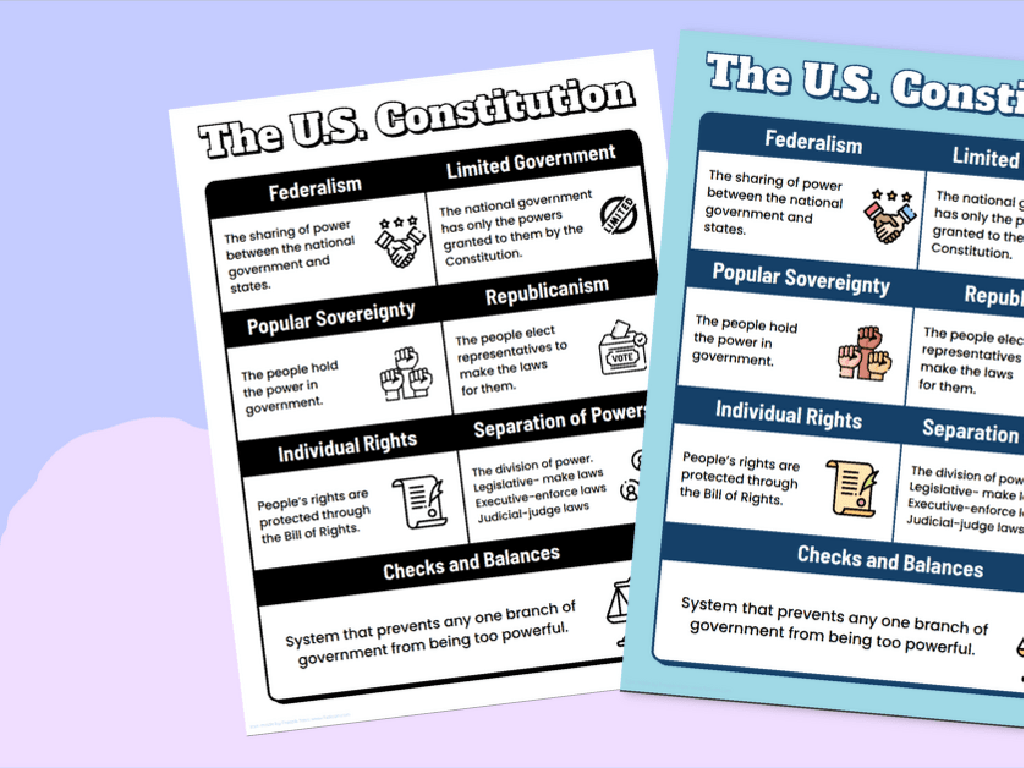
Understanding the U.S. Constitution
– The Constitution: U.S. law foundation
– It’s the supreme law that outlines government structure and rights.
– A ‘Living Document’
– It adapts over time through amendments to reflect societal changes.
– Constitution Structure
– It’s organized into a Preamble, 7 Articles, and 27 Amendments.
– Preamble, Articles, Amendments
|
The U.S. Constitution is the foundational document of the United States, establishing the framework of the federal government and outlining the rights of citizens. It is often referred to as a ‘Living Document’ because it can be amended to adapt to new circumstances and the evolving needs of the country. The Constitution is divided into three main parts: the Preamble, which states the purpose of the document; the Articles, which describe the structure of the government; and the Amendments, which are changes or additions made over time. The first ten amendments are known as the Bill of Rights. When discussing the Constitution with students, emphasize its importance in everyday life and how it continues to impact laws and rights. Encourage them to think about how the Constitution remains relevant today and the process by which it can be amended.
The Bill of Rights: Safeguarding Freedom
– The First 10 Amendments explained
– The Bill of Rights consists of the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution, serving as a cornerstone for American freedoms.
– Designed to protect individual liberties
– These amendments were created to guarantee essential rights and prevent government overreach.
– Freedom of Speech: a fundamental right
– This right allows individuals to express ideas without government restraint.
– Right to a Fair Trial: ensuring justice
– A cornerstone of the legal system, guaranteeing a fair legal process to the accused.
|
This slide introduces the Bill of Rights, which are the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. They were ratified to protect individual liberties against infringement by the government. Key examples include the Freedom of Speech, which allows citizens to speak freely without fear of government censorship or punishment, and the Right to a Fair Trial, which is fundamental to the American justice system, ensuring that every person receives a fair and public hearing. Discuss each right in detail, providing historical context and current relevance. Encourage students to think of ways these rights impact their daily lives and the functioning of democracy.
The Three Branches of Government
– Legislative Branch role
– Congress makes and amends federal laws.
– Executive Branch role
– The President and federal agencies enforce laws.
– Judicial Branch role
– Supreme Court interprets and reviews laws.
– Balance of power
|
This slide introduces the three distinct branches of the U.S. Government as outlined in the Constitution, each with its own responsibilities and powers. The Legislative Branch, composed of the House of Representatives and the Senate, creates laws. The Executive Branch, headed by the President, enforces these laws. The Judicial Branch, led by the Supreme Court, interprets laws and their constitutionality. It’s crucial for students to understand the concept of checks and balances, which ensures that no single branch becomes too powerful. Discuss examples of how these branches interact, such as how a bill becomes a law, how the executive can veto legislation, and how the judiciary can rule laws unconstitutional.
The Court System in the United States
– Federal vs. State Courts
– Federal courts handle national laws, state courts handle state laws.
– Supreme Court’s Role
– The Supreme Court reviews lower court decisions, ensures laws comply with the Constitution.
– Journey of a Court Case
– Cases start in lower courts and can be appealed to higher courts.
– Significance of Court Hierarchy
|
This slide aims to provide students with a clear understanding of the structure and function of the U.S. court system. It distinguishes between federal and state courts, emphasizing the types of laws each handles. The role of the Supreme Court is explained as the final authority on legal disputes and constitutional interpretation. Students will learn how cases can move from trial courts to appellate courts and possibly to the Supreme Court. Emphasize the importance of the court hierarchy in ensuring a consistent and fair judicial process. Use real-life examples to illustrate how a case progresses through the system, and discuss landmark Supreme Court cases to highlight its pivotal role in American law and society.
Laws in Our Daily Lives
– School rules and consequences
– Examples: Attendance, homework policies
– Home and community laws
– Curfews, local ordinances
– Laws ensure safety
– Traffic laws prevent accidents
– Upholding order in society
– Laws help resolve conflicts
|
This slide aims to make students aware of the pervasive nature of laws in everyday life. Begin by discussing the rules students follow at school, such as attendance and homework policies, and the consequences of not adhering to them. Extend the conversation to laws at home, like household rules, and in the community, such as curfews and local ordinances. Emphasize the importance of laws in maintaining safety, using examples like traffic laws designed to prevent accidents. Finally, discuss how laws help uphold order in society by providing a framework to resolve conflicts and maintain peace. Encourage students to think of additional examples where laws impact their daily lives and to consider how different laws are necessary for different settings.
Landmark Supreme Court Cases
– Marbury v. Madison: Judicial Review
– Established the principle of judicial review in U.S. courts
– Brown v. Board of Education: Desegregation
– Declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional
– Miranda v. Arizona: Miranda Rights
– Required police to inform suspects of their rights before questioning
|
This slide introduces students to three landmark Supreme Court cases that have shaped American law and society. Marbury v. Madison established the Supreme Court’s power to declare laws unconstitutional, thus introducing the concept of judicial review. Brown v. Board of Education was a pivotal moment in the civil rights movement, overturning the ‘separate but equal’ doctrine and starting the process of desegregation in schools. Miranda v. Arizona led to the creation of ‘Miranda rights,’ ensuring that suspects are aware of their rights to silence and an attorney during police interrogations. Encourage students to discuss the impact of these cases on American society and consider how these decisions continue to affect us today.
Becoming an Informed Citizen
– Know your rights and duties
– Understand the Bill of Rights and your civic duties.
– Stay updated on laws
– Follow news, debates, and legal changes.
– Engage in civic matters
– Vote, volunteer, and join community discussions.
– Impact of informed citizenship
– Informed citizens contribute to a healthy democracy.
|
This slide aims to emphasize the importance of being an informed citizen in a democratic society. Students should understand their rights as outlined in the Bill of Rights, as well as their responsibilities, such as obeying laws and paying taxes. Staying informed about new laws and legal issues is crucial for meaningful participation in society. Encourage students to engage in civic life through voting, volunteering, and participating in community discussions. Highlight how informed citizens can influence government and society, and why their contribution is vital for the functioning of a healthy democracy.
Class Activity: Mock Trial Experience
– Apply knowledge in a mock trial
– Students role-play court case positions
– Students take on roles like judge, jury, attorneys, and witnesses
– Engage in trial process discussion
– Discuss the steps and roles in a trial
– Reflect on the learning experience
– Share thoughts on the justice system and trial procedures
|
This interactive class activity is designed to consolidate students’ understanding of laws and courts by having them participate in a mock trial. Students will be assigned different roles within the court system, allowing them to actively engage with the material and apply what they’ve learned about the judicial process. After the role-play, facilitate a class discussion to reflect on the trial process, the roles they played, and their perspectives on the justice system. This will help students to critically analyze the legal procedures and their importance in upholding the law. Possible activities include trying a historical case, a fictional scenario, or a current event issue. Ensure that each student understands their role and has the resources they need to perform it effectively.