Washington'S Presidency: Part I
Subject: Social studies
Grade: Eighth grade
Topic: The Early Republic
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Introduction to the Early Republic
– Significance of the Early Republic
– The formative period post-Independence
– George Washington’s pivotal role
– First President, set precedents for others
– Exploring Washington’s presidency
– Study his policies, challenges, and impacts
– Anticipating key learnings
|
This slide introduces the Early Republic, a critical time when the United States was establishing its identity as a nation. Emphasize the significance of this era as the foundation of American democracy. Discuss George Washington’s role as the first President and how his decisions shaped the presidency and the nation. Outline what students will learn about his presidency, including his policies, the challenges he faced, and the lasting impacts of his leadership. Encourage students to think critically about how Washington’s presidency still influences the United States today.
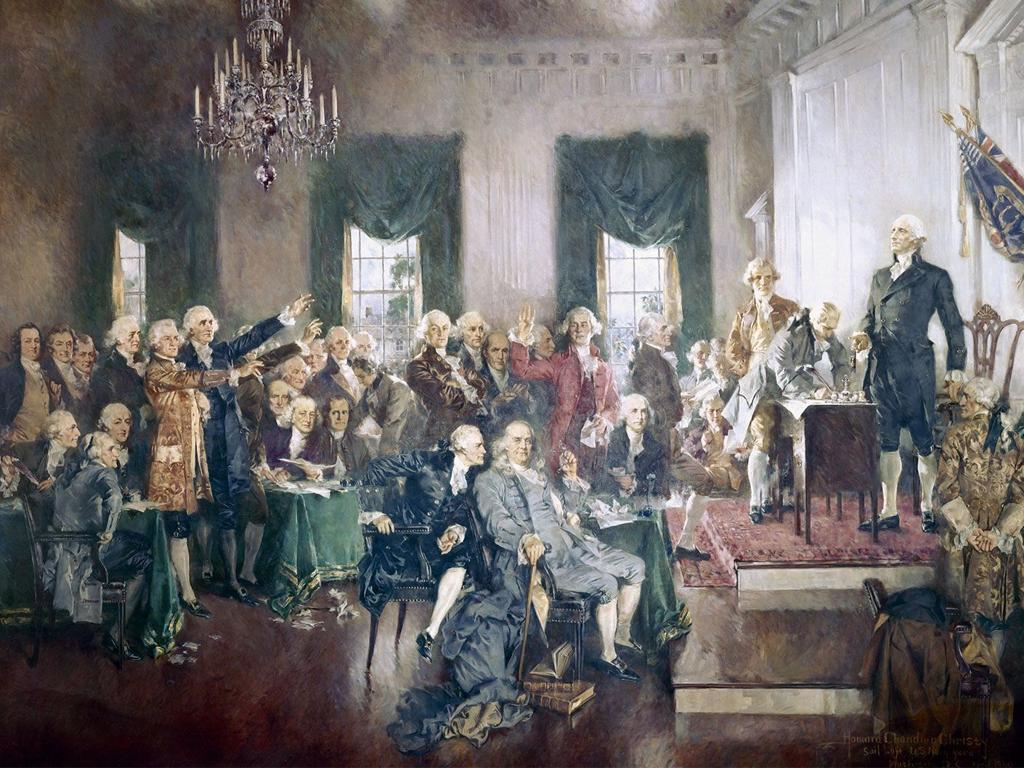
George Washington: The First President
– Washington’s path to presidency
– Led Revolutionary War, presided over Constitutional Convention
– 1789 election: Unanimous victory
– First U.S. presidential election, Washington won all electoral votes
– Setting presidential precedents
– Established many traditions, including two-term limit, Cabinet system
– Washington’s enduring legacy
– His decisions shaped the executive role for future leaders
|
This slide introduces students to George Washington’s significant role in American history, focusing on his journey to becoming the first President of the United States. Highlight Washington’s leadership during the Revolutionary War and his key role in the Constitutional Convention, which paved the way for his presidency. Discuss the election of 1789, emphasizing the unanimity of his election as a testament to his widespread respect and popularity. Explore the precedents Washington set, such as the establishment of the Cabinet and the two-term limit, which have had lasting impacts on the presidency. Encourage students to consider how Washington’s actions and decisions during his presidency have shaped the executive branch and the overall governance of the country.
Challenges of Washington’s Presidency
– Establishing a new government
– Setting up the first U.S. federal government was a complex task with no precedent.
– Maintaining neutrality abroad
– Washington aimed to keep the U.S. impartial during foreign conflicts, especially between Britain and France.
– Creating a stable financial system
– He had to address national debt and lay the foundation for economic growth and stability.
|
This slide outlines the major challenges faced by George Washington during his presidency. As the first President, he had the daunting task of establishing a functioning federal government from scratch. This involved creating departments, setting precedents, and defining the role of the presidency. Internationally, Washington’s policy of neutrality was crucial in maintaining peace and allowing the young nation to grow without the entanglement of European wars. Economically, Washington, with the help of his Treasury Secretary Alexander Hamilton, worked to create a stable financial system, which included managing the national debt and establishing a national bank. These challenges were foundational in shaping the future of the United States.
Washington’s Cabinet: Shaping the New Government
– Formation of the first Cabinet
– Established to advise the President on various matters
– Key figures: Hamilton and Jefferson
– Hamilton: Treasury Secretary, Jefferson: State Secretary
– Cabinet’s role in policy-making
– Developed fiscal policies and foreign relations
– Cabinet’s influence on governance
– Set precedents for future administrations
|
This slide aims to introduce students to the origins and functions of the Presidential Cabinet during George Washington’s presidency. Emphasize the Cabinet’s role in advising the President and its impact on shaping the nation’s early policies and governance. Highlight key figures like Alexander Hamilton, the first Secretary of the Treasury, who played a pivotal role in establishing the nation’s financial system, and Thomas Jefferson, the first Secretary of State, who influenced foreign policy. Discuss how their differing viewpoints on how the government should be run led to the formation of political parties. The Cabinet’s actions under Washington set many precedents that defined the executive branch’s operations in subsequent administrations.
The Bill of Rights: Foundation of Freedom
– Significance of the first 10 amendments
– The amendments outline fundamental rights and freedoms.
– Protection of individual liberties
– They safeguard freedom of speech, religion, and more.
– Ratification process under Washington
– States debated and voted to adopt these crucial amendments.
– Bill of Rights in modern context
– Understanding its relevance to our lives today.
|
The Bill of Rights, consisting of the first ten amendments to the Constitution, is a cornerstone of American democracy, highlighting the importance of individual freedoms and legal protections. These amendments were ratified during George Washington’s presidency, reflecting the young nation’s commitment to civil liberties. The process of ratification involved debates and votes by the states, ensuring a broad consensus. In today’s lesson, we’ll explore each amendment’s role in protecting citizens’ rights and how these rights continue to impact our daily lives. Encourage students to think about how the Bill of Rights affects them personally and to consider its importance in current events.
The Whiskey Rebellion: Testing Federal Power
– Conflict over whiskey tax
– Farmers resisted the tax on distilled spirits, leading to rebellion.
– Washington’s decisive response
– Washington led troops to suppress the rebellion, showing federal resolve.
– Strengthening federal authority
– The successful suppression emphasized the federal government’s power.
– Rebellion’s resolution significance
– The peaceful resolution set a precedent for handling domestic issues.
|
The Whiskey Rebellion was a pivotal moment in the early United States, where the new government faced internal conflict over a federal tax on whiskey. This tax was particularly burdensome for frontier farmers, who often distilled their grain into whiskey. The rebellion tested the federal government’s ability to enforce its laws. President George Washington’s decision to personally lead federal troops to quell the rebellion was a significant demonstration of federal power and authority. It showed that the government would not tolerate violent resistance to its laws. The resolution of the rebellion without widespread bloodshed also set an important precedent for the peaceful resolution of civil disputes, reinforcing the rule of law in the young nation. Discuss with students how this event helped to define the authority of the federal government and its ability to enforce laws across all states.
Foreign Policy: Neutrality Proclamation
– Debate over foreign wars
– Should America join foreign conflicts?
– Neutrality Proclamation 1793
– Washington’s declaration to remain neutral
– Proclamation’s impact
– Set precedent for avoiding entanglement
– Shaping American policy
– Influenced U.S. policy for years to come
|
This slide delves into the early challenges faced by the United States regarding its stance on foreign conflicts. The debate over whether to participate in foreign wars was a significant issue during Washington’s presidency. The Neutrality Proclamation of 1793 was a landmark decision by President George Washington that established the U.S.’s position of neutrality in the ongoing European conflicts, particularly between France and Britain. This proclamation had a lasting effect on American foreign policy, setting a precedent for non-involvement that influenced the nation’s diplomatic decisions well into the future. Discuss with students how this stance was both a strategic move to protect the nation’s interests and a reflection of the desire to focus on domestic growth and stability.
Washington’s Farewell Address
– Washington’s 2-term tradition
– Set the precedent for a two-term limit for U.S. presidents
– Highlights of the Farewell Address
– Warned against political parties and foreign alliances
– Farewell Address’s lasting impact
– Shaped U.S. foreign policy and political culture
– Influence on future presidencies
– Established norms for presidential transitions and policies
|
George Washington’s decision not to seek a third term established an important tradition for the presidency, which later became law with the 22nd Amendment. His Farewell Address, delivered in 1796, contained key points that have had a lasting influence on the nation, such as the dangers of political factions and the importance of neutrality in foreign affairs. This address has been considered a guiding document for future presidents and has impacted the way the highest office conducts itself both domestically and internationally. Encourage students to reflect on how Washington’s decisions and advice continue to resonate in contemporary politics.
Role-Play: Washington’s Presidency
– Form groups for role-play
– Each group picks a key figure/event
– Examples: Washington’s inauguration, the Whiskey Rebellion, or the creation of the National Bank
– Perform a skit on the chosen topic
– Discuss modern handling of events
– Compare past strategies with today’s political approaches
|
This class activity is designed to engage students with the historical figures and events of Washington’s presidency through interactive role-play. By dividing the class into groups, each group will select a significant figure or event from that era to dramatize. Possible topics include Washington’s inauguration, the Whiskey Rebellion, or the establishment of the National Bank. After the performances, lead a discussion on how these events might be handled in the current political climate, encouraging students to think critically about the evolution of governance and decision-making. This activity will help students better understand the historical context and its relevance to today’s world.