Select Parts Of A Topographic Map
Subject: Science
Grade: Seventh grade
Topic: Topographic Maps
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Welcome to Topographic Maps!
– Earth’s surface features
– Earth has mountains, valleys, plains, and bodies of water.
– Defining topographic maps
– A topographic map represents Earth’s 3D features on a 2D surface using contour lines.
– Uses of topographic maps
– They help hikers, engineers, and scientists understand terrain.
– Importance in various fields
– Essential for planning buildings, hiking trips, and scientific research.
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of topographic maps and their significance in understanding the Earth’s surface. Begin by discussing the various features of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains and valleys. Explain that a topographic map is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief, usually using contour lines. Emphasize how these maps are crucial tools for a wide range of activities, from outdoor recreation to urban planning. Encourage students to think about how different professionals might use topographic maps in their work and to consider the importance of accurate representation of the Earth’s terrain.
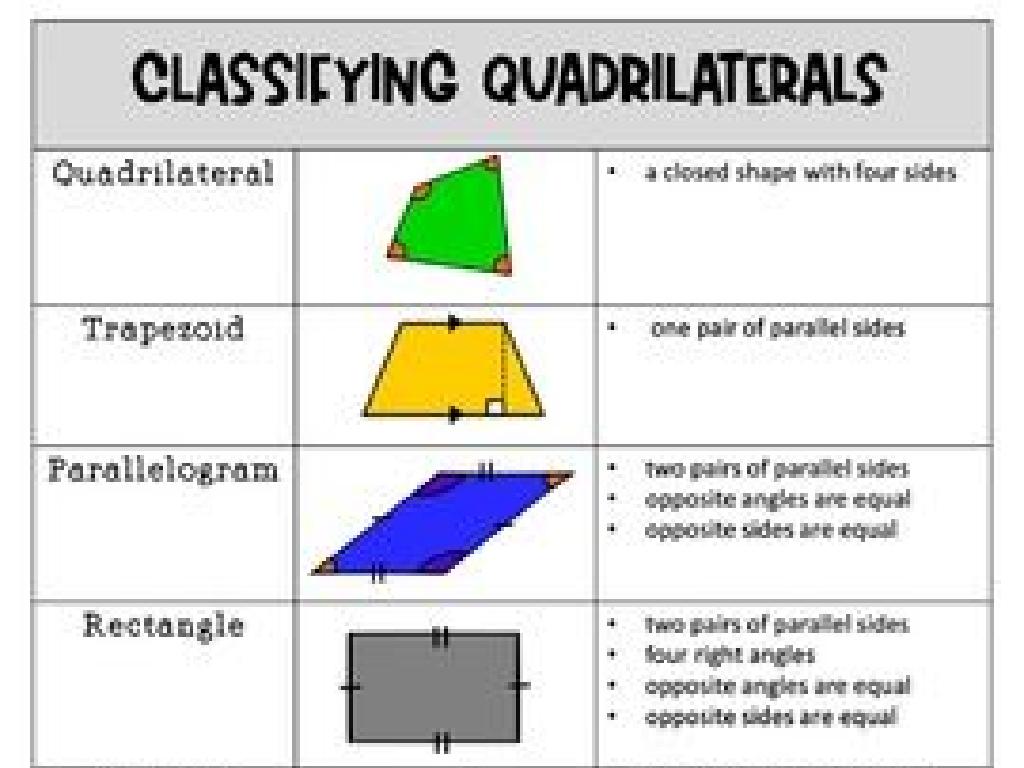
Key Features of Topographic Maps
– Understanding map symbols
– Symbols represent physical features like rivers, mountains.
– Reading the map scale
– Scale shows the ratio of a distance on the map to the actual ground.
– Significance of the legend
– The legend decodes symbols and scale for better map reading.
|
This slide aims to familiarize students with the essential elements of topographic maps, which are crucial for interpreting the map’s information accurately. Symbols are the language of topographic maps, representing various physical landforms and man-made structures. The map scale is a tool that helps translate the dimensions on the map to real-world distances, which is vital for navigation and understanding the scope of the terrain. The legend acts as a key to unlock the meanings of the symbols and scale, guiding the reader to comprehend the map fully. Encourage students to practice by looking at different symbols and scales and using the legend to interpret them. This foundational knowledge will be instrumental in their further studies of geography and earth sciences.
Contours and Elevation on Topographic Maps
– Contour lines represent elevation
– Lines that show height above sea level
– Elevation and relief explained
– Elevation is height; relief is the difference in height
– Determining terrain steepness
– Close lines mean steep; spread out lines mean flat
– Practice reading contour lines
|
This slide introduces students to the concept of contour lines on topographic maps, which are used to represent elevation. Elevation refers to the height above sea level, while relief indicates the variations in elevation across a surface. By examining the spacing between contour lines, students can determine the steepness of the terrain; closer lines indicate steeper slopes. Encourage students to practice by looking at different topographic maps and identifying areas of varying steepness. This will help them visualize how contour lines depict the shape and elevation of the land.
Reading Topographic Maps
– Identify map landforms
– Recognize hills, valleys, and plateaus on the map
– Calculate slope with contours
– Use contour lines to determine the steepness of terrain
– Navigate using topography
– Apply map reading to find the best routes for travel
– Understanding map symbols
|
This slide introduces students to the basics of reading topographic maps, an essential skill in earth sciences and geography. Students should learn to recognize various landforms such as hills, valleys, and plateaus by their representation on a map. Calculating the slope is crucial for understanding the terrain’s steepness, which can be done by examining the spacing of contour lines – closer lines indicate a steeper slope. Navigating using a topographic map is a practical skill that involves applying knowledge of contour lines and map symbols to determine the best travel routes. Ensure students understand the symbols commonly used on these maps to represent different features.
Activity: Create Your Own Contour Map!
– Gather materials: clay, floss, cardboard, markers
– Build a 3D clay model of a landscape
– Shape hills, valleys, and other features with clay
– Use dental floss to slice model into layers
– Each slice represents a different elevation level
– Draw contour lines on cardboard to represent layers
– Contour lines show elevation changes on a flat map
|
This hands-on activity is designed to help students understand the concept of topographic maps by creating their own. Students will use clay to build a 3D model of a landscape, which they will then slice horizontally with dental floss to represent different elevation levels. After slicing, students will transfer these levels onto cardboard by drawing contour lines that correspond to each layer of the model. This visual and tactile experience reinforces the understanding of how topographic maps represent three-dimensional terrains on two-dimensional surfaces. For the teacher: Prepare a step-by-step guide for building the model, ensure all materials are available, and consider different landscapes students can model. Have examples of real topographic maps for comparison.
Map Reading Challenge: Topographic Explorers
– Pair up for map feature identification
– Find and label hills, valleys, rivers, and other features
– Use map scale for distance calculation
– Measure between landmarks and convert using the scale
– Present findings to the class
– Share what you’ve learned about the map’s terrain
|
This class activity is designed to engage students with practical skills in reading and interpreting topographic maps. Students will work in pairs to foster collaboration and peer learning. They should identify various physical features such as hills, valleys, and water bodies, using symbols and contour lines. Using the map’s scale, they will calculate the actual distance between points of interest. This exercise will help them understand scale representation and distance measurement on maps. After completing the tasks, each pair will present their findings, enhancing their communication skills and reinforcing their understanding of topographic maps. Possible activities include identifying the highest point on the map, the source of a river, or the pattern of a mountain range.
Topographic Maps: Conclusion & Recap
– Review map features
Contours, symbols, scale, and legend are essential features.
– Significance of map skills
Map reading is vital for navigation and understanding geography.
– Engage in Q&A session
Clarify doubts and solidify understanding through questions.
– Summarize key learnings
|
This slide aims to consolidate the students’ knowledge of topographic maps by reviewing the key features such as contour lines, symbols, scale, and the legend. Emphasize the importance of map reading skills in various real-life scenarios, such as hiking or planning a route. The Q&A session is crucial for addressing any uncertainties students may have and ensuring they have a firm grasp of the concepts. Summarize the session by reiterating the main points and encouraging students to continue exploring and practicing their map reading skills.