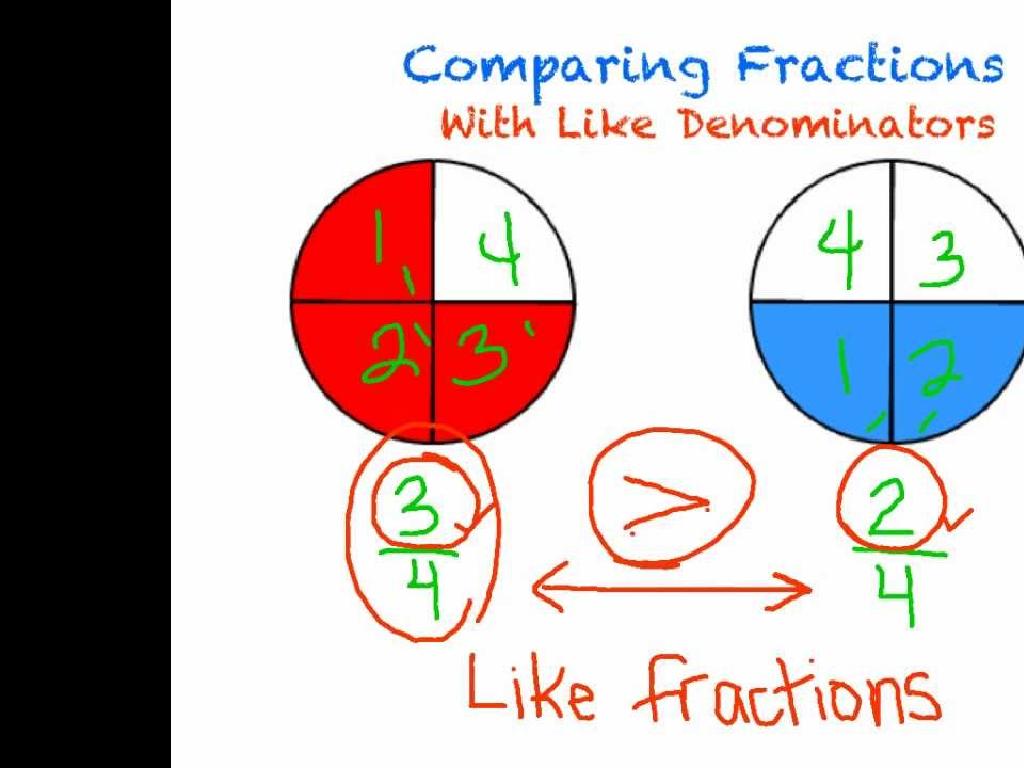
Make Arrays To Model Multiplication
Subject: Math
Grade: Third grade
Topic: Understand Multiplication
Please LOG IN to download the presentation. Access is available to registered users only.
View More Content
Welcome to Multiplication!
– Learn about multiplication
– Multiplication as repeated addition
– If you have 4 groups of 3, it’s like 3 + 3 + 3 + 3
– Using arrays for multiplication
– Arrays show this in rows and columns, like seats in a theater
– Practice with real examples
– Let’s multiply 2 rows of 4 apples each to find the total
|
This slide introduces the concept of multiplication to third graders. Begin by explaining that multiplication is a quick way of adding the same number several times. Use everyday examples like counting apples or arranging chairs in rows to illustrate the point. Show how arrays can visually represent multiplication problems, making it easier to understand. Encourage the students to create their own arrays with different objects to reinforce the concept. Provide hands-on activities where they can practice forming arrays and solving multiplication problems. This will help solidify their understanding of multiplication as repeated addition.
Understanding Multiplication with Arrays
– Multiplication: a basic math operation
– Combines equal groups together
– Like adding the same number over and over
– Example: 3 groups of 2 apples
– 3 x 2 means 3 groups of 2 apples each
– Visualize with arrays: 3 rows of 2
– Draw 3 rows with 2 apples in each row to show 3 x 2
|
This slide introduces the concept of multiplication as a fundamental math operation, emphasizing its role in combining equal groups to find a total amount. Use the example of apples to illustrate how multiplication works in a context familiar to third graders. Explain that multiplication is similar to adding the same number multiple times. To help students visualize multiplication, introduce the concept of arrays, which are an arrangement of objects in rows and columns. For the example given, demonstrate how to draw an array with 3 rows and 2 columns to represent 3 groups of 2 apples, which equals 6 apples in total. Encourage students to create their own arrays with different numbers to further understand multiplication.
Making Arrays to Model Multiplication
– Arrays visualize multiplication
– Rows and columns make arrays
– Think of rows as groups of items, and columns as how many in each group
– Each array spot equals one unit
– If we have 3 rows of 4 spots, it’s like 3 groups of 4 units
– Practice with different arrays
– Try creating arrays with candies or toys to understand multiplication
|
This slide introduces the concept of arrays as a visual tool to help students understand and model multiplication. Explain that an array is made up of rows and columns, and each spot in the array represents one unit. Use concrete examples like arranging candies or toys in rows and columns to show how this represents multiplication (e.g., 3 rows of 4 candies represents 3×4). Encourage students to practice by creating their own arrays with different numbers of rows and columns to solidify their understanding of how multiplication works.
Arrays in Real Life
– Arrays are all around us
– Think of egg cartons or a chessboard
– Discover arrays in everyday life
– Look for patterns like rows and columns at home or in class
– Arrays simplify counting
– Instead of counting one by one, we can use multiplication
– Practice with real-life arrays
|
This slide aims to help students recognize arrays in their daily environment and understand how they relate to multiplication. Arrays are a visual representation of multiplication concepts, making it easier for students to grasp the idea of counting objects in groups. Encourage students to find and draw arrays they see around them, such as in egg cartons (2×6 array) or a chessboard (8×8 array). Explain how these arrays can be counted quickly using multiplication (e.g., 2 rows of 6 eggs is 2×6=12 eggs in total). This practical application helps solidify the concept of multiplication and prepares them for more complex problems. During the next class, students can share the arrays they found and discuss how they used multiplication to count the total number of items.
Creating Your Own Arrays
– Select objects for your array
– Organize objects in rows and columns
– Use multiplication to find total objects
– If you have 2 rows of 5, it’s 2 times 5, which equals 10
– Example: 3 rows of 4 apples
– 3 rows of 4 apples is 3 times 4, so you have 12 apples in total
|
This slide is an activity for students to create their own arrays to understand multiplication conceptually. Students should choose any small objects they can easily arrange and count. They will organize these objects into rows and columns, which will visually represent a multiplication problem. For example, if they create an array with 3 rows and 4 objects in each row, they can count by fours (4, 8, 12) to find the total. This hands-on activity helps solidify the concept of multiplication as repeated addition. Encourage students to try different combinations of rows and columns and to share their arrays with the class. Provide guidance on how to arrange objects neatly and how to count them efficiently using multiplication.
Practice Time: Let’s Make Arrays!
– Create arrays using stickers
– Each student receives stickers
– Think of the multiplication fact
– If you have 3 rows of 4 stickers, it shows 3×4
– Share what your array represents
– Explain your array to the class
|
This activity is designed to help students visualize multiplication through the use of arrays. Distribute stickers to each student and instruct them to arrange their stickers in rows and columns to create arrays. Guide them to observe how the number of rows and the number of stickers in each row can represent a multiplication fact. For example, if a student creates an array with 3 rows and 4 stickers in each row, this can be seen as 3 groups of 4, which corresponds to the multiplication fact 3×4=12. Encourage students to share their arrays with the class and explain the multiplication fact it represents. This will reinforce their understanding of multiplication as repeated addition and the concept of arrays as a visual representation of this operation.
Array Scavenger Hunt Activity
– Find classroom items in arrays
– Pair up and list your array finds
– Write multiplication for each array
– Example: 4 rows of 5 apples is 4 x 5
– Share your findings with the class
|
This interactive activity is designed to help students recognize arrays in their everyday environment and understand how they can represent multiplication. Students should work in pairs to encourage collaboration. They will look around the classroom to find objects arranged in an array format, such as desks, windows, or tiles. Once they find an array, they should make a list and then write the corresponding multiplication sentence for that array. For example, if there are 4 rows of 5 apples on a shelf, the multiplication sentence would be 4 x 5. After the hunt, each pair will share their findings with the class, explaining how they determined the multiplication sentence for each array. This will reinforce their understanding of arrays and how they model multiplication. Provide guidance and ensure that each pair has at least one example to share. Possible variations for different pairs could include finding arrays of different sizes or shapes, or even creating their own arrays with classroom materials.
Review and Reflect: Arrays and Multiplication
– Recap: Multiplication with arrays
Arrays show multiplication as groups of rows and columns.
– Arrays assist multiplication understanding
They turn abstract multiplication into visual groups.
– Finding arrays in our homes
Look for patterns like egg cartons or a chessboard.
– Sharing our array examples
|
This slide aims to consolidate the students’ understanding of using arrays to model multiplication. Begin by reviewing how arrays represent multiplication as equal groups arranged in rows and columns, making it easier to visualize and solve problems. Emphasize that arrays help in understanding the concept of multiplication by providing a clear picture of what multiplying numbers actually means. Encourage students to think about and identify arrays they come across in everyday life, such as egg cartons (2×6) or a set of chairs arranged in rows. This will help them relate the mathematical concept to the real world. Conclude by asking students to share examples of arrays they’ve found at home, fostering a connection between their environment and mathematical concepts.
Homework Challenge: Array Multiplication
– Take home your array worksheet
– Create 5 unique arrays at home
– Use objects like coins or buttons to form arrays
– Write a multiplication sentence
– Example: 3 rows of 4 coins is 3 x 4
– Share your arrays in class
|
This homework task is designed to reinforce the concept of arrays in multiplication by allowing students to create physical representations using everyday items. Encourage creativity in finding objects to use for their arrays. Remind them that an array is a set of objects arranged in rows and columns, and each row should have the same number of objects. The multiplication sentence represents the total number of objects, with one factor being the number of rows and the other the number of objects in each row. In the next class, students will have the opportunity to present their arrays and explain the multiplication sentences they wrote, fostering a deeper understanding of the concept through teaching and peer learning.